A Comprehensive Analysis Of Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Issues In Server Environments
A Comprehensive Analysis of Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Issues in Server Environments
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Analysis of Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Issues in Server Environments
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Analysis of Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Issues in Server Environments. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Analysis of Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Issues in Server Environments

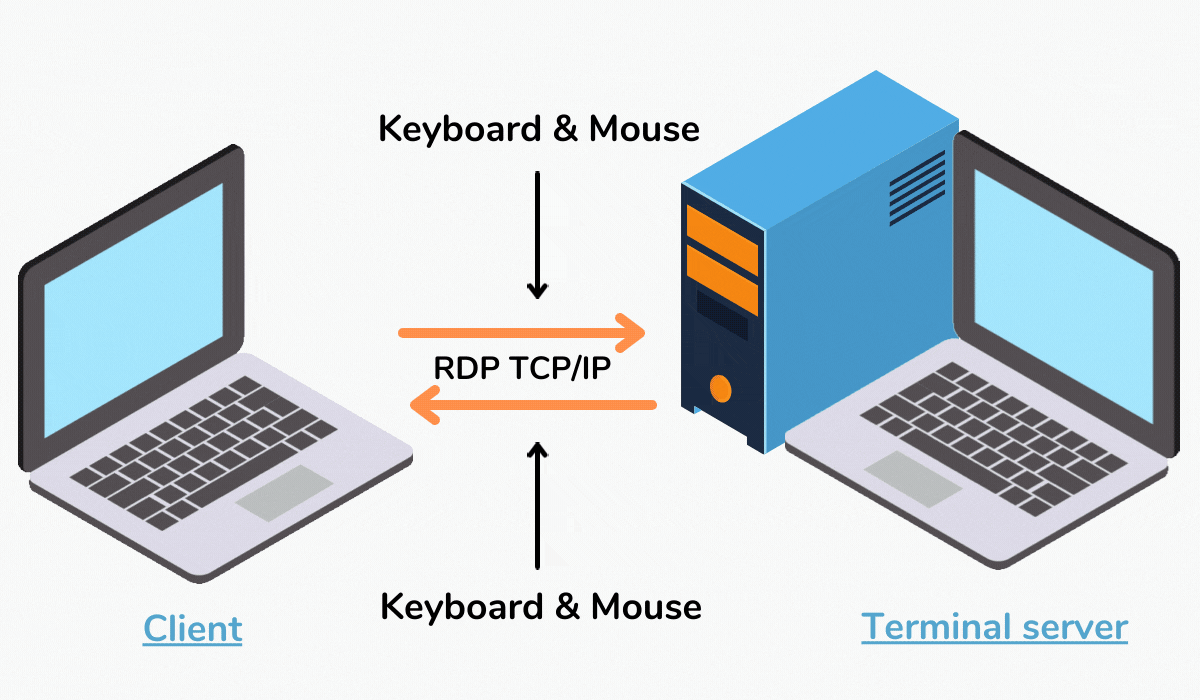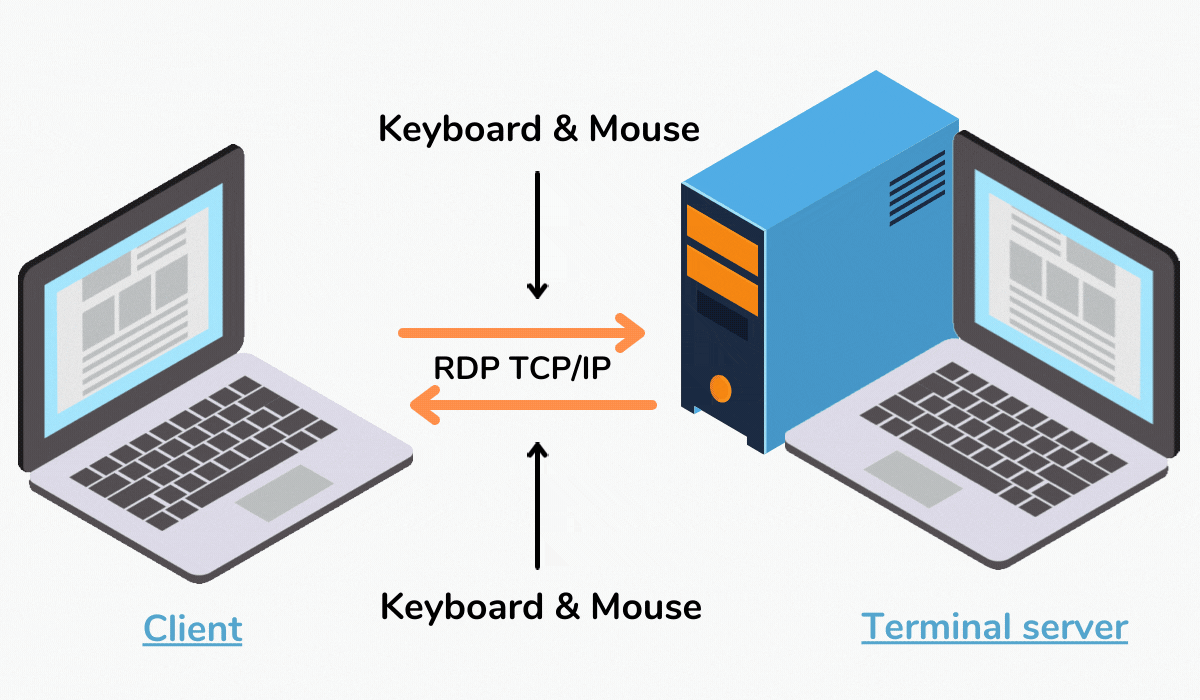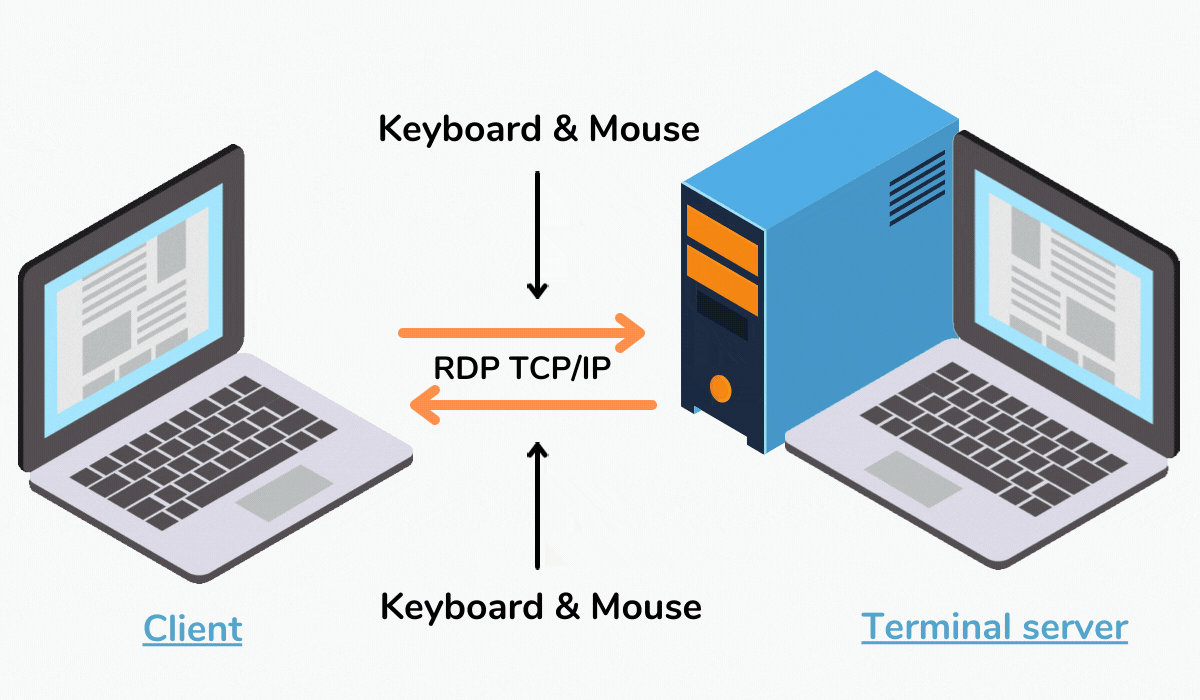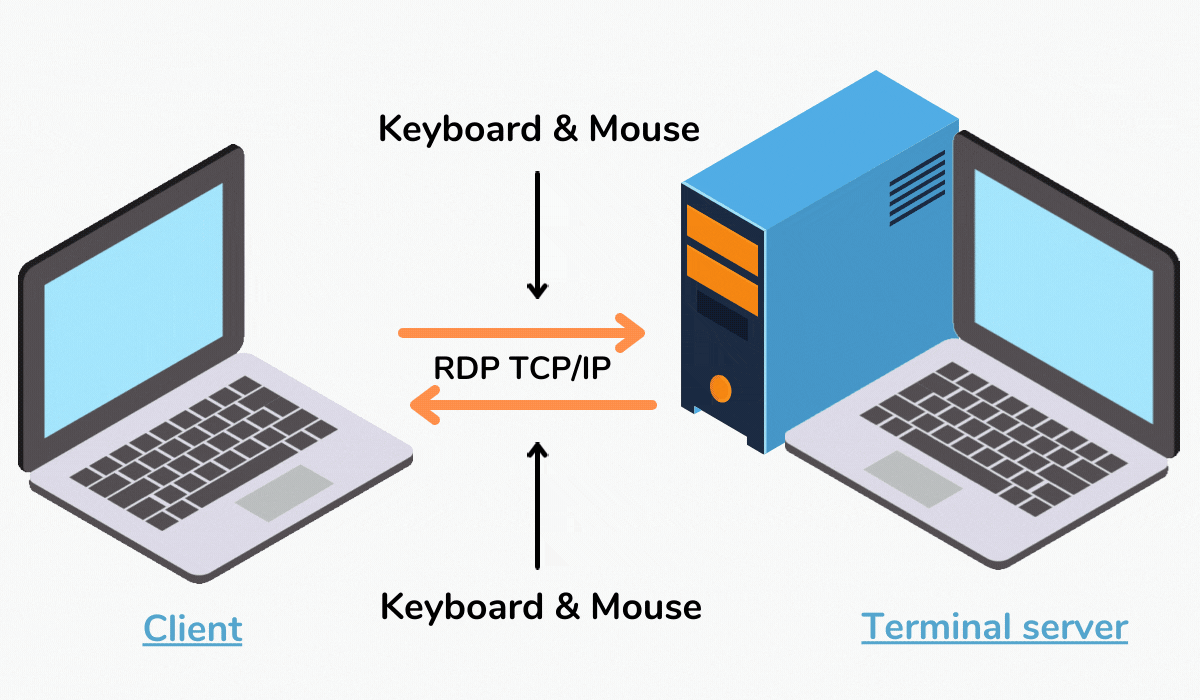
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a crucial technology for managing and accessing server environments remotely. Its ability to provide a secure and reliable connection to remote machines has made it an indispensable tool for IT professionals and system administrators. However, despite its widespread use and inherent benefits, RDP can sometimes encounter issues, leading to frustrating interruptions in workflow and productivity. One such issue that has garnered considerable attention is the phenomenon of RDP sessions freezing, which can significantly impact server management and user experience. This article delves into the intricacies of RDP freeze, exploring its potential causes, troubleshooting strategies, and preventative measures to minimize its occurrence.
Understanding RDP Freeze: A Deep Dive
RDP freeze refers to a state where the remote desktop connection abruptly stops responding, rendering the connected server inaccessible. The user interface becomes unresponsive, and all actions cease, effectively freezing the session. This issue can manifest in various ways, ranging from a complete freeze of the entire session to a specific window or application becoming unresponsive.
Potential Causes of RDP Freeze
The root cause of RDP freeze can be multifaceted, stemming from a combination of factors related to both the client and server machines.
-
Server-Side Factors:
- High CPU Utilization: When the server is heavily burdened with resource-intensive tasks, it may struggle to allocate sufficient processing power to the RDP session, resulting in a freeze.
- Insufficient Memory: Limited RAM can lead to performance bottlenecks, impacting the responsiveness of the RDP session.
- Network Connectivity Issues: Intermittent or unstable network connections can disrupt the data flow between the client and server, causing the RDP session to freeze.
- Hardware Failures: Faulty network cards, hard drives, or other hardware components can contribute to RDP freeze.
- Software Conflicts: Incompatible or outdated drivers, applications, or operating system updates can create conflicts, leading to session freezes.
- Excessive Disk I/O: High disk activity, particularly during large file transfers or database operations, can overload the server, causing RDP sessions to freeze.
- Security Software Interference: Overly aggressive security software can sometimes interfere with RDP connections, resulting in freezes.
-
Client-Side Factors:
- Insufficient Bandwidth: Limited network bandwidth can hinder the smooth flow of data, causing RDP sessions to freeze.
- Client Hardware Limitations: Outdated or underpowered client machines may struggle to keep up with the demands of the RDP session, leading to freezes.
- Client Software Conflicts: Conflicts between client software and the RDP client can disrupt the connection, resulting in a freeze.
- Network Latency: High latency, especially over long distances or unstable connections, can introduce delays that contribute to RDP freezes.
Troubleshooting RDP Freeze: A Systematic Approach
Addressing RDP freeze necessitates a systematic approach, carefully analyzing potential causes and implementing appropriate solutions.
-
Identify the Scope of the Freeze: Determine whether the freeze affects all RDP sessions or is specific to a particular client machine. This will help narrow down the potential causes.
-
Check Server Resources: Monitor the server’s CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk activity. Identify any significant resource constraints that could be contributing to the freeze.
-
Review Network Connectivity: Ensure a stable network connection between the client and server. Test network speed and latency to identify any bottlenecks.
-
Analyze Event Logs: Review the server’s event logs for any error messages or warnings related to RDP or other system events that might offer insights into the cause of the freeze.
-
Disable Security Software: Temporarily disable any security software on both the client and server machines to rule out potential interference.
-
Update Drivers and Software: Ensure that all drivers, especially network drivers, and software are up to date. Outdated drivers can cause conflicts and lead to freezes.
-
Check for Hardware Issues: Perform hardware diagnostics to rule out any faulty components that might be contributing to the freeze.
-
Optimize Server Settings: Adjust server settings to improve performance and minimize resource contention. This may involve tweaking RDP settings, limiting the number of concurrent sessions, or adjusting memory allocation.
-
Consider Alternative Connection Methods: If RDP freeze persists, explore alternative remote access solutions like SSH or VNC, which may offer better stability in certain scenarios.
Preventative Measures to Minimize RDP Freeze
Proactive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of RDP freeze:
-
Maintain Server Resources: Ensure sufficient CPU, memory, and disk space to handle the demands of RDP sessions. Regular monitoring and resource optimization are crucial.
-
Prioritize Network Stability: Maintain a reliable and high-bandwidth network connection between the client and server. Consider using dedicated network connections or VPNs for enhanced stability.
-
Implement Regular Updates: Keep the server and client operating systems, drivers, and applications updated to address security vulnerabilities and improve compatibility.
-
Minimize Resource-Intensive Tasks: Avoid running resource-intensive applications on the server during active RDP sessions. Schedule such tasks for off-peak hours or utilize dedicated resources.
-
Configure RDP Settings: Optimize RDP settings to balance performance and security. Adjust settings like connection quality, color depth, and compression level to reduce bandwidth consumption and improve responsiveness.
-
Implement a Monitoring System: Use monitoring tools to track server performance metrics, including CPU utilization, memory usage, and network activity. This allows for early detection and mitigation of potential issues before they lead to RDP freezes.
FAQs on RDP Freeze
Q: What are some common signs of an RDP freeze?
A: Common signs include:
- The cursor becoming unresponsive.
- Windows becoming unresponsive to mouse clicks or keyboard inputs.
- Applications failing to respond or becoming unresponsive.
- The entire RDP session becoming unresponsive, with no visible progress.
Q: How can I tell if the RDP freeze is caused by a server or client issue?
A: To determine the source of the freeze, check the following:
- Server-Side: If multiple RDP clients experience freezes simultaneously, it’s likely a server issue.
- Client-Side: If the freeze occurs only on a specific client machine, it’s more likely a client-related issue.
Q: Can I use RDP to troubleshoot RDP freeze?
A: While it’s possible to use RDP to troubleshoot a freeze, it’s generally not recommended as the frozen RDP session itself might be the source of the issue. Consider alternative remote access methods like SSH or VNC for troubleshooting.
Q: How can I prevent RDP freeze from happening again?
A: Implementing preventive measures like maintaining server resources, prioritizing network stability, and configuring RDP settings appropriately can significantly reduce the occurrence of RDP freeze.
Q: What are the potential consequences of an RDP freeze?
A: RDP freeze can have various consequences, including:
- Interruption of Work: Frozen sessions disrupt workflows and prevent users from accessing critical information or completing tasks.
- Loss of Productivity: Downtime caused by RDP freeze can lead to significant productivity losses.
- Data Loss: In extreme cases, prolonged RDP freeze can lead to data loss if unsaved work is lost due to the session disruption.
- Security Risks: If the freeze is caused by a security breach, it can expose sensitive data to unauthorized access.
Tips for Managing RDP Freeze
- Implement a robust monitoring system: Regularly monitor server resources, network connectivity, and RDP session performance to identify potential issues early.
- Maintain a stable network connection: Ensure a high-bandwidth and reliable network connection between the client and server.
- Optimize server performance: Ensure sufficient CPU, memory, and disk space to handle the demands of RDP sessions.
- Regularly update software and drivers: Keep the server and client operating systems, drivers, and applications updated to address security vulnerabilities and improve compatibility.
- Implement security measures: Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and keep security software up to date to protect against unauthorized access.
Conclusion
RDP freeze is a complex issue that can stem from various factors, both on the server and client sides. Addressing this issue requires a systematic approach, involving careful troubleshooting and preventative measures. By understanding the potential causes, implementing effective troubleshooting strategies, and prioritizing preventative measures, organizations can significantly minimize the occurrence of RDP freeze and ensure a smooth and reliable remote access experience for their users.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Analysis of Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Issues in Server Environments. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!