A Comprehensive Guide To Windows Server 2022 Remote Desktop Services (RDS)
A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Server 2022 Remote Desktop Services (RDS)
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Server 2022 Remote Desktop Services (RDS)
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Server 2022 Remote Desktop Services (RDS). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Server 2022 Remote Desktop Services (RDS)

The world of work is increasingly mobile and remote, demanding flexible and secure solutions for accessing applications and data. Windows Server 2022 Remote Desktop Services (RDS) provides a powerful and reliable platform to meet these needs, enabling organizations to deliver virtualized desktops and applications to users anywhere, anytime.
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of setting up and managing Windows Server 2022 RDS, outlining its key features, benefits, and practical considerations.
Understanding the Fundamentals of RDS
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is a suite of technologies that allows users to access virtualized desktops and applications remotely. This empowers organizations to:
- Centralize and manage desktops and applications: Instead of individually configuring and maintaining each user’s machine, RDS allows administrators to manage all desktops and applications from a central location, streamlining IT operations and reducing maintenance costs.
- Enhance security: RDS enables secure access to corporate resources, with robust authentication and authorization mechanisms in place. Data is centrally stored and managed, reducing the risk of data loss or unauthorized access.
- Improve user experience: RDS provides a consistent and reliable user experience across various devices, allowing users to access their workspaces from any location with a stable internet connection.
- Boost productivity: Users can seamlessly access their applications and files, regardless of their location, fostering greater flexibility and productivity.
- Optimize resource utilization: RDS allows organizations to leverage existing hardware resources effectively, reducing the need for expensive desktop hardware upgrades and minimizing energy consumption.
Key Components of Windows Server 2022 RDS
Windows Server 2022 RDS comprises several key components working in tandem:
- Remote Desktop Session Host (RD Session Host): This server role hosts the virtualized desktops and applications, providing the core functionality of RDS.
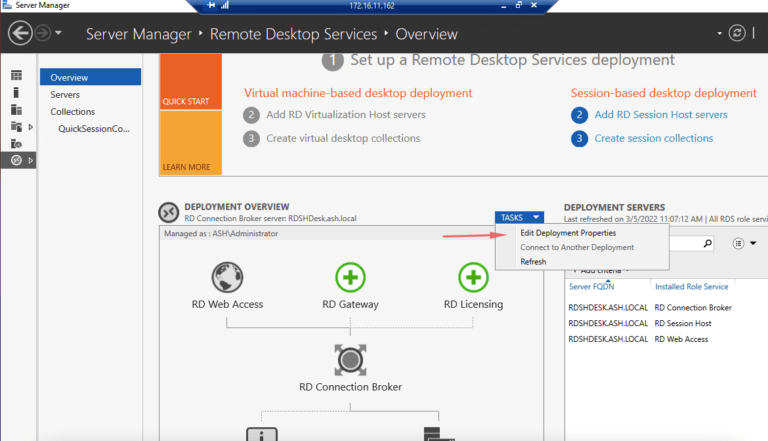
- Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway): This server role acts as a secure entry point for remote users, enabling them to connect to the RDS infrastructure through a firewall.
- Remote Desktop Licensing Server (RD Licensing Server): This server role manages and issues licenses for RDS users, ensuring compliance with Microsoft licensing agreements.
- Remote Desktop Connection Broker (RD Connection Broker): This server role acts as a central point for user connections, managing user sessions and directing them to available RD Session Host servers.
- Remote Desktop Web Access (RD Web Access): This component allows users to access their virtual desktops and applications through a web browser, eliminating the need for dedicated desktop clients.
Setting up Windows Server 2022 RDS
Setting up Windows Server 2022 RDS involves a series of steps, each requiring careful consideration and configuration:
-
Prepare the Infrastructure:
- Hardware Requirements: Ensure that your server hardware meets the minimum specifications for running RDS. Consider the number of users and the resource demands of the applications being deployed.
- Operating System: Install Windows Server 2022 on your chosen server hardware.
- Network Configuration: Configure your network infrastructure to support RDS, including firewall rules and network segmentation for security.
-
Install RDS Roles:
- RD Session Host: Install the RD Session Host role on the server that will host the virtualized desktops and applications.
- RD Gateway: Install the RD Gateway role on a server that will provide secure access for remote users.
- RD Licensing Server: Install the RD Licensing Server role on a dedicated server to manage and issue licenses.
- RD Connection Broker: Install the RD Connection Broker role on a server that will manage user connections and session allocation.
-
Configure RDS Roles:
- RD Session Host: Configure the RD Session Host to define the virtual desktops and applications that will be available to users. This includes setting up user profiles, creating virtual desktops, and configuring applications.
- RD Gateway: Configure the RD Gateway to define the access policies and authentication methods for remote users. This includes configuring firewall rules, setting up SSL certificates for secure communication, and defining user authentication methods.
- RD Licensing Server: Configure the RD Licensing Server to define the licensing model for RDS users, including the number of users and the type of licenses required.
- RD Connection Broker: Configure the RD Connection Broker to define the connection rules for user sessions, including the load balancing mechanism and the allocation of users to available RD Session Host servers.
-
Deploy and Test RDS:
- Deploy virtual desktops and applications: Deploy the virtual desktops and applications that users will access through RDS. This includes installing the required software and configuring the applications to work within the RDS environment.
- Test the RDS infrastructure: Thoroughly test the RDS infrastructure to ensure that users can successfully connect to the virtual desktops and applications, and that the performance meets the required standards.
Benefits of Using Windows Server 2022 RDS
Deploying Windows Server 2022 RDS offers numerous advantages for organizations:
- Enhanced Security: RDS provides a secure environment for accessing corporate resources, with robust authentication and authorization mechanisms in place. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Improved User Experience: RDS delivers a consistent and reliable user experience across various devices, allowing users to access their workspaces from any location with a stable internet connection.
- Increased Productivity: Users can seamlessly access their applications and files, regardless of their location, fostering greater flexibility and productivity.
- Cost Savings: RDS allows organizations to leverage existing hardware resources effectively, reducing the need for expensive desktop hardware upgrades and minimizing energy consumption.
- Simplified Management: RDS centralizes the management of desktops and applications, streamlining IT operations and reducing maintenance costs.
Best Practices for Optimizing RDS Performance
To ensure optimal performance and user experience, follow these best practices:
- Optimize Network Bandwidth: Ensure sufficient bandwidth to support the number of users and the resource demands of the applications being deployed.
- Utilize Load Balancing: Implement load balancing to distribute user sessions across available RD Session Host servers, maximizing resource utilization and minimizing performance bottlenecks.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor the performance of the RDS infrastructure to identify and address any performance issues proactively.
- Regularly Update Software: Keep all RDS components and underlying operating systems up-to-date with the latest security patches and performance enhancements.
- Implement User Profile Optimization: Optimize user profiles to reduce the size and load time of user data, improving the user experience and overall system performance.
FAQs Regarding Windows Server 2022 RDS
1. What are the hardware requirements for running Windows Server 2022 RDS?
The hardware requirements for running Windows Server 2022 RDS depend on the number of users, the resource demands of the applications being deployed, and the desired level of performance. It is recommended to consult the official Microsoft documentation for detailed hardware specifications.
2. How do I secure access to RDS resources?
RDS provides several security features, including:
- Network Level Authentication (NLA): Requires users to authenticate before connecting to the RD Session Host, preventing unauthorized access.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Can be implemented to enhance security by requiring users to provide two forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code.
- Firewall Rules: Configure firewall rules to restrict access to RDS resources to authorized users and devices.
- SSL Certificates: Use SSL certificates to encrypt communication between users and the RD Gateway, ensuring secure data transmission.
3. How do I manage user profiles in RDS?
RDS provides several options for managing user profiles, including:
- Centralized User Profiles: Store user profiles centrally on the RD Session Host, ensuring consistency across different sessions.
- Roaming User Profiles: Allow user profiles to roam between different devices, enabling users to access their personalized settings regardless of the device they are using.
- Folder Redirection: Redirect specific user folders, such as My Documents or Desktop, to a central location, simplifying profile management and reducing storage requirements.
4. What are the licensing requirements for RDS?
RDS requires users to have valid licenses to access virtual desktops and applications. The licensing model depends on the number of users and the type of licenses required. Refer to the Microsoft licensing documentation for detailed information on RDS licensing.
5. How do I troubleshoot RDS issues?
RDS provides several tools and resources for troubleshooting issues:
- Event Viewer: Check the Event Viewer for error messages related to RDS components.
- Performance Monitor: Use Performance Monitor to monitor the performance of RDS components and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Remote Desktop Services Manager: Use Remote Desktop Services Manager to manage and troubleshoot RDS components.
- Microsoft Documentation: Consult the official Microsoft documentation for troubleshooting guides and solutions to common RDS issues.
Tips for Successful RDS Implementation
- Plan Carefully: Define your specific requirements, including the number of users, the applications to be deployed, and the desired level of performance.
- Pilot Test: Conduct a pilot test with a small group of users to identify and resolve any potential issues before a full rollout.
- Monitor and Optimize: Regularly monitor the performance of the RDS infrastructure and make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal performance and user experience.
- Provide User Training: Train users on how to access and use RDS resources effectively.
Conclusion
Windows Server 2022 Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is a powerful and versatile solution for delivering virtualized desktops and applications to users remotely. By leveraging its features and following best practices, organizations can enhance security, improve user experience, increase productivity, and optimize resource utilization.
RDS empowers organizations to adapt to the evolving demands of the modern workplace, enabling employees to work effectively from anywhere, anytime, while maintaining a secure and efficient IT environment.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Windows Server 2022 Remote Desktop Services (RDS). We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!