A Comprehensive Look At The Evolution Of Windows Server: From Its Inception To The Future
A Comprehensive Look at the Evolution of Windows Server: From Its Inception to the Future
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at the Evolution of Windows Server: From Its Inception to the Future
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at the Evolution of Windows Server: From Its Inception to the Future. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at the Evolution of Windows Server: From Its Inception to the Future

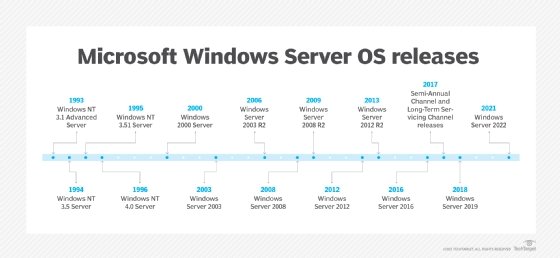
Windows Server, a cornerstone of modern computing infrastructure, has undergone a continuous evolution since its inception. This journey, marked by significant advancements and adaptations, has consistently aimed to address the ever-changing demands of businesses and organizations. Understanding this evolution provides valuable insights into the capabilities and benefits of Windows Server, offering a historical perspective on its role in shaping the technological landscape.
The Genesis of Windows Server: Windows NT 3.1 (1993)
The foundation for Windows Server was laid with the release of Windows NT 3.1 in 1993. This operating system, initially targeted at enterprise environments, introduced a robust kernel and a stable platform for server applications. It marked a departure from the consumer-focused Windows 3.1, emphasizing stability, security, and scalability. Key features included:
- Preemptive multitasking: Enabling multiple applications to run concurrently without interfering with each other.
- Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP): Supporting multiple processors for enhanced performance.
- Win32 API: Providing a consistent programming interface for application development.
- Security features: Including user accounts, access control lists, and auditing capabilities.
Windows NT 3.5 and 3.51 (1994-1995): Refinement and Enhancements
Windows NT 3.5, released in 1994, focused on enhancing stability and performance. It introduced features like:
- Improved network support: Enhanced TCP/IP and IPX/SPX networking capabilities.
- Support for additional hardware: Expanding compatibility with a wider range of devices.
- Windows NT Workstation: A version designed for individual users, offering a more familiar interface.
Windows NT 3.51, released in 1995, addressed minor bugs and improved performance, further solidifying the platform’s stability.
Windows NT 4.0 (1996): A Milestone in Server Evolution
Windows NT 4.0, released in 1996, represented a significant leap forward for the platform. This version incorporated features that significantly impacted server administration and user experience:
- Active Directory (AD): A centralized directory service for managing users, computers, and resources, revolutionizing network administration.
- Internet Information Services (IIS): A web server platform, enabling the hosting of websites and web applications.
- Terminal Services: Allowing remote access to the server, enhancing user flexibility.
- Enhanced security features: Further strengthening the platform’s security posture.
Windows 2000 Server (2000): A Focus on Integration and Stability
Windows 2000 Server, released in 2000, aimed to integrate the best features of Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 98, providing a more unified and stable platform. Key enhancements included:
- Improved Active Directory: Enhancements to Active Directory, including support for domain trusts and group policies.
- Enhanced network support: Improved networking capabilities, including support for VPNs and IPv6.
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI): A standardized interface for managing system resources.
- Performance improvements: Optimization for improved performance and scalability.
Windows Server 2003 (2003): Innovation and Expansion
Windows Server 2003, released in 2003, introduced significant innovations and expanded upon the existing features, solidifying its position as a leading enterprise server platform. Notable features included:
- .NET Framework: A platform for building web services and applications, enabling greater interoperability.
- Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD RMS): Enhancing data protection and information security.
- Hyper-V virtualization: Allowing multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on a single server, optimizing resource utilization.
- Windows Server Update Services (WSUS): Centralized management of software updates for improved security and stability.
Windows Server 2008 (2008): A Shift Towards Cloud Computing
Windows Server 2008, released in 2008, marked a significant shift towards cloud computing, emphasizing virtualization, scalability, and management capabilities. Key features included:
- Enhanced Hyper-V: Improved virtualization capabilities, enabling larger virtual machines and greater performance.
- Server Core installation: A minimal installation option, reducing the attack surface and simplifying management.
- Windows PowerShell: A scripting language for automating administrative tasks, streamlining server management.
- Windows Azure: A cloud computing platform for deploying and managing applications in the cloud.
Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009): Refinement and Stability
Windows Server 2008 R2, released in 2009, focused on refining the platform’s stability, performance, and security. It introduced features like:
- Enhanced Hyper-V: Further improvements to virtualization, including support for live migration of virtual machines.
- Branch Office Direct Access: Providing secure remote access for branch offices.
- Windows Server AppFabric: A platform for developing and managing applications in a cloud environment.
Windows Server 2012 (2012): Embracing Modernization
Windows Server 2012, released in 2012, embraced modernization, focusing on cloud-native applications, automation, and enhanced security. Key features included:
- Windows Server 2012 Essentials: A simplified version for small businesses, offering easy setup and management.
- Windows Azure Pack: Enabling the creation of private cloud environments on-premises.
- Windows Server Update Services (WSUS): Further enhancements for centralized management of software updates.
- Enhanced security features: Including support for BitLocker Drive Encryption and AppLocker.
Windows Server 2012 R2 (2013): Consolidation and Optimization
Windows Server 2012 R2, released in 2013, consolidated and optimized the platform, building upon the foundation laid by Windows Server 2012. It introduced features like:
- Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials: Enhanced features for small businesses, including remote access and cloud integration.
- Windows Azure Pack: Continued development of private cloud capabilities.
- Windows Server Update Services (WSUS): Continued enhancements for centralized management of software updates.
- Enhanced security features: Including support for Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Network Access Protection (NAP).
Windows Server 2016 (2016): A Focus on Hybrid Cloud
Windows Server 2016, released in 2016, shifted its focus towards hybrid cloud environments, enabling organizations to seamlessly integrate on-premises infrastructure with cloud services. Key features included:
- Nano Server: A minimal installation option, further reducing the attack surface and simplifying management.
- Windows Server Containers: Enabling the deployment of containerized applications, promoting portability and scalability.
- Windows Server Update Services (WSUS): Continued enhancements for centralized management of software updates.
- Enhanced security features: Including support for Shielded Virtual Machines and Host Guardian Service.
Windows Server 2019 (2019): Embracing Modernization and Security
Windows Server 2019, released in 2019, continued the focus on modernization and security, incorporating the latest advancements in cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and security. Key features included:
- Azure Stack HCI: A hyperconverged infrastructure solution, simplifying on-premises infrastructure management.
- Windows Server Containers: Continued development of containerized applications, enhancing portability and scalability.
- Windows Admin Center: A unified interface for managing Windows Server environments, simplifying administration.
- Enhanced security features: Including support for Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) and Azure Sentinel.
Windows Server 2022 (2022): A New Era of Security and Innovation
Windows Server 2022, released in 2022, marked a significant leap forward, introducing a new generation of security features, performance enhancements, and cloud-native capabilities. Key features included:
- Azure Arc: Enabling the management of on-premises infrastructure from the Azure portal, enhancing flexibility and scalability.
- Windows Server Containers: Continued development of containerized applications, promoting portability and scalability.
- Windows Admin Center: Continued development of the unified management interface, simplifying administration.
- Enhanced security features: Including support for Secured-core PCs, Hyper-V enhancements for security, and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) integration for improved identity management.
The Future of Windows Server: Embracing Innovation and Adaptability
The future of Windows Server lies in its ability to adapt to the ever-changing technological landscape. Continued focus on cloud-native capabilities, automation, security, and AI integration will be crucial in shaping the platform’s future. Microsoft’s commitment to innovation, coupled with its focus on providing a secure and reliable platform, positions Windows Server as a key player in the future of computing.
FAQs about Windows Server Version History
1. What is the difference between Windows NT and Windows Server?
Windows NT was the original name for the server operating system, later renamed to Windows Server. While Windows NT focused on enterprise environments, Windows Server further emphasized server-specific features and capabilities.
2. When was the first version of Windows Server released?
The first version of Windows Server, known as Windows NT 3.1, was released in 1993.
3. What is the latest version of Windows Server?
The latest version of Windows Server is Windows Server 2022, released in 2022.
4. What are the key features of Windows Server 2022?
Windows Server 2022 introduces a new generation of security features, performance enhancements, and cloud-native capabilities, including Azure Arc, Secured-core PCs, Hyper-V enhancements for security, and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) integration for improved identity management.
5. What are the benefits of using Windows Server?
Windows Server offers a robust, secure, and scalable platform for businesses and organizations, providing a wide range of features and capabilities for managing infrastructure, applications, and data.
Tips for Understanding Windows Server Version History
- Focus on key features: Identify the major features and advancements introduced with each version of Windows Server.
- Consider the context: Understand the technological landscape and the challenges addressed by each version.
- Explore documentation: Consult Microsoft’s official documentation for detailed information about each version.
- Engage with the community: Join online forums and communities to learn from other users and experts.
Conclusion
The history of Windows Server is a testament to its adaptability and resilience. From its humble beginnings as Windows NT 3.1 to the modern, cloud-native capabilities of Windows Server 2022, the platform has consistently evolved to meet the changing needs of businesses and organizations. As technology continues to advance, Windows Server remains a cornerstone of modern computing infrastructure, offering a powerful and reliable platform for managing critical workloads and ensuring business continuity. Understanding its history provides valuable insights into its capabilities and benefits, offering a clear perspective on its role in shaping the technological landscape.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at the Evolution of Windows Server: From Its Inception to the Future. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!