Data Security And Performance Enhancement: A Comprehensive Guide To RAID Configurations In Windows Server
Data Security and Performance Enhancement: A Comprehensive Guide to RAID Configurations in Windows Server
Related Articles: Data Security and Performance Enhancement: A Comprehensive Guide to RAID Configurations in Windows Server
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Data Security and Performance Enhancement: A Comprehensive Guide to RAID Configurations in Windows Server. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Data Security and Performance Enhancement: A Comprehensive Guide to RAID Configurations in Windows Server
The foundation of any robust server infrastructure lies in the security and reliability of its data storage. Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) technology has long been a cornerstone for achieving this objective, offering a range of configurations tailored to specific needs. As technology evolves, so too do the best practices for implementing RAID in Windows Server environments. This article explores the essential considerations for maximizing data protection and performance in Windows Server, focusing on the latest advancements and practical strategies.
Understanding the Fundamentals of RAID
At its core, RAID is a method of combining multiple physical hard drives into a single logical unit, enhancing data storage capabilities. This approach offers several key advantages:
- Data Redundancy: RAID configurations provide data redundancy, safeguarding against disk failures by storing data across multiple drives. This redundancy ensures data availability even if one or more drives fail.
- Enhanced Performance: RAID configurations can significantly improve I/O performance, particularly for read operations, by distributing data across multiple drives, leading to faster data access.
- Increased Storage Capacity: Some RAID levels allow for the creation of a larger logical storage volume than the sum of the individual physical drive capacities.
Choosing the Right RAID Level for Your Needs
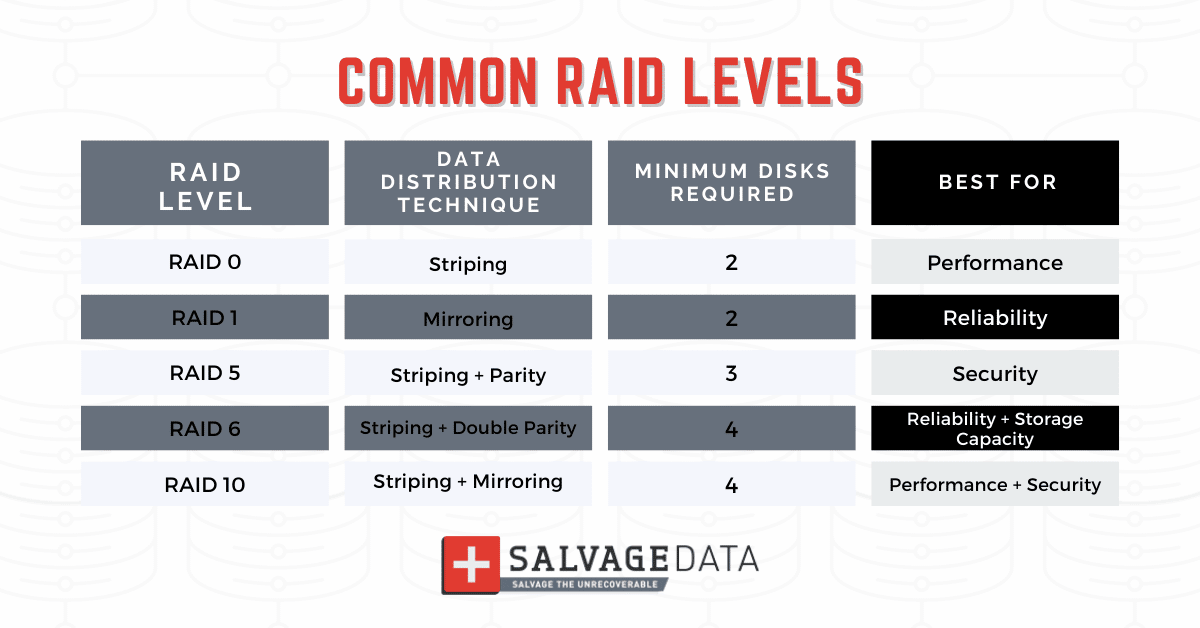
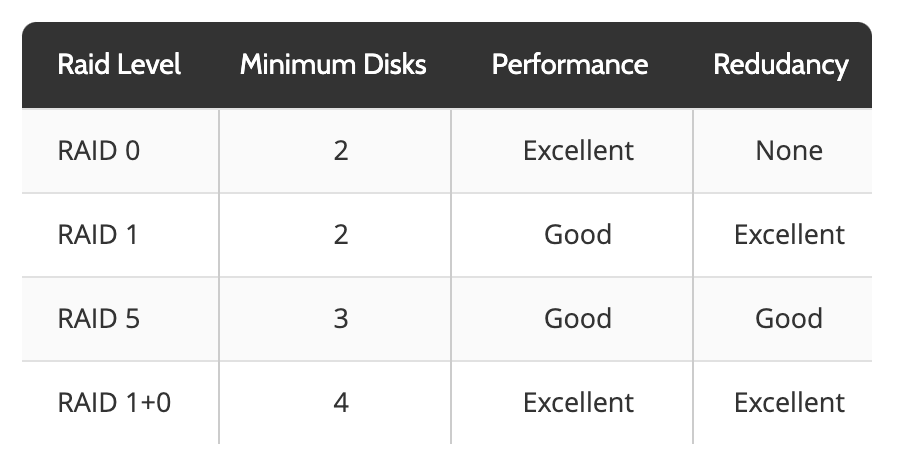
The choice of RAID level depends on the specific requirements of your application and the desired balance between data protection and performance. The most common RAID levels are:
- RAID 0 (Striping): RAID 0 splits data across multiple drives, offering the highest performance but no data redundancy. A single drive failure results in data loss.
- RAID 1 (Mirroring): RAID 1 creates an exact copy of data on two or more drives, providing maximum data protection. However, it utilizes twice the storage space compared to a single drive.
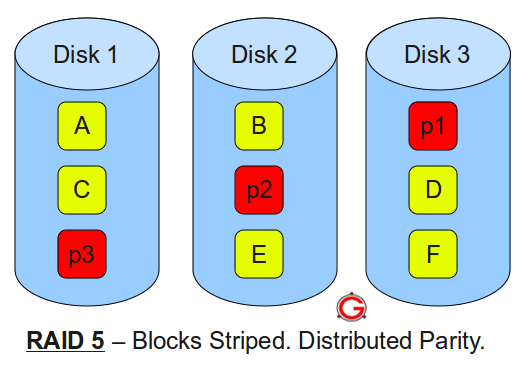
- RAID 5 (Striping with Parity): RAID 5 distributes data and parity information across multiple drives, offering a balance between performance and redundancy. A single drive failure can be tolerated without data loss.
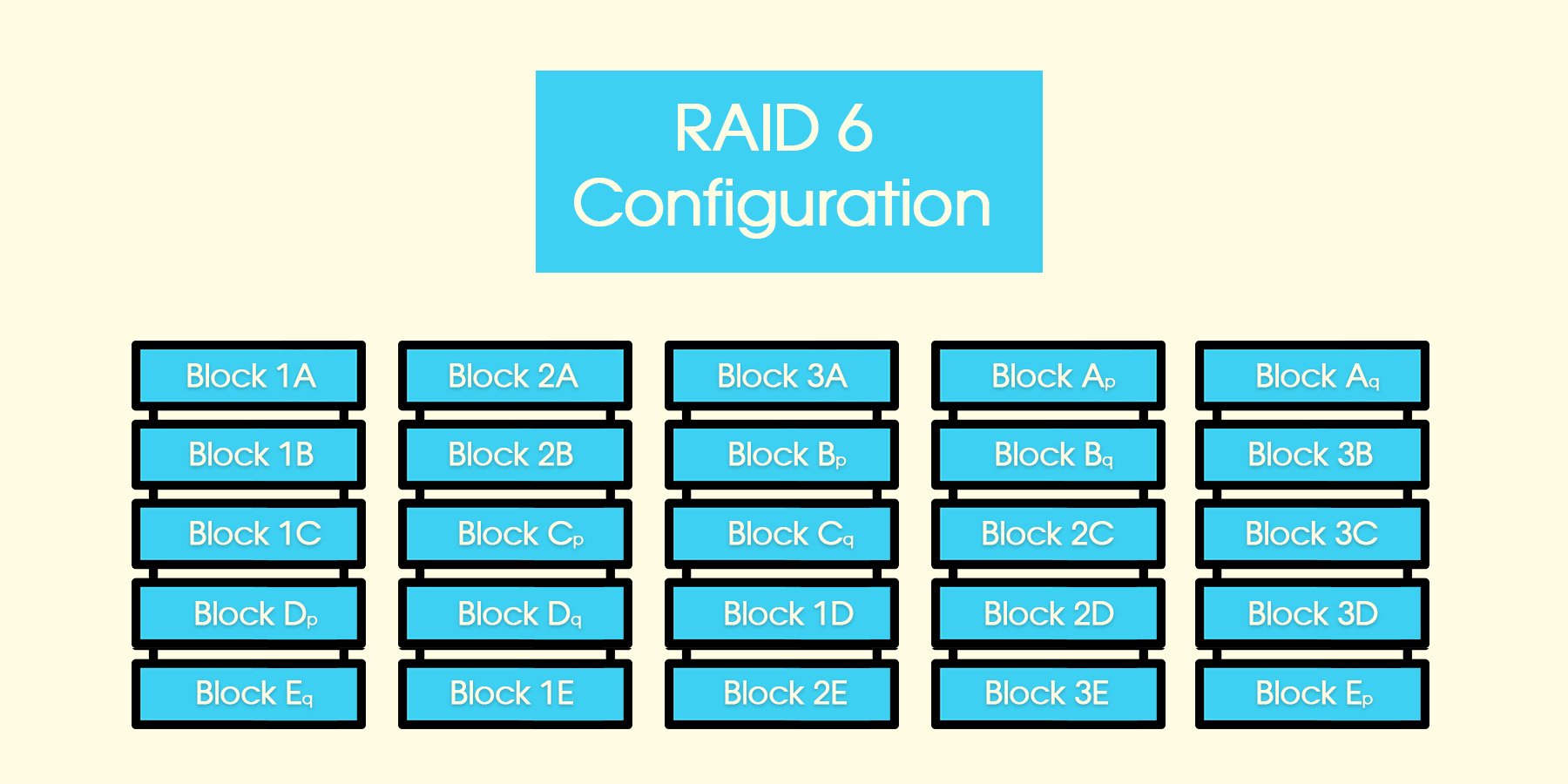
- RAID 6 (Striping with Dual Parity): RAID 6 provides even higher data protection than RAID 5, allowing for the failure of two drives without data loss. However, it comes at the cost of reduced performance compared to RAID 5.
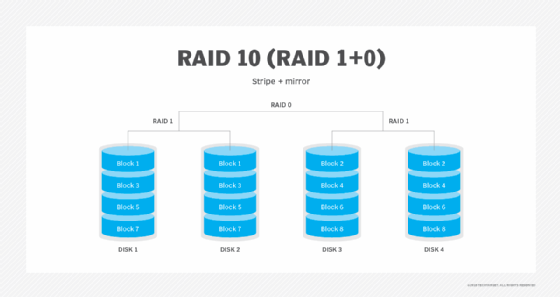
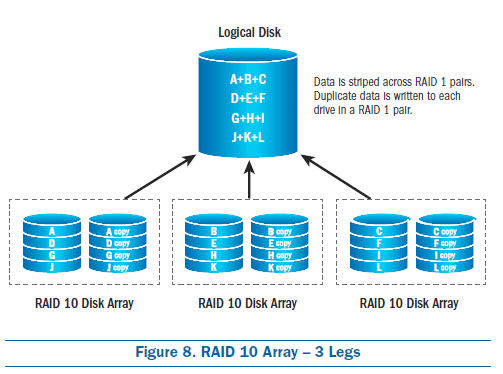
- RAID 10 (Mirroring and Striping): RAID 10 combines the advantages of both RAID 1 and RAID 0, offering high performance and data redundancy. It requires at least four drives and is ideal for applications with high I/O demands and critical data.
Best Practices for Implementing RAID in Windows Server
- Choose the Right RAID Level: Carefully consider the specific needs of your applications, data sensitivity, and performance requirements when selecting the appropriate RAID level.
- Use High-Quality Drives: Invest in high-quality, reliable hard drives from reputable manufacturers to minimize the risk of drive failures.
- Use a Dedicated RAID Controller: Employ a dedicated RAID controller for enhanced performance and reliability compared to software-based RAID solutions.
- Implement Proper Backup Strategies: RAID provides data protection against drive failures but does not protect against other data loss scenarios such as accidental deletion or malware attacks. Implement comprehensive backup strategies to safeguard against these threats.
- Monitor RAID Performance and Health: Regularly monitor the performance and health of your RAID configuration using tools provided by your RAID controller or Windows Server.
- Consider RAID 10 for Critical Applications: For applications requiring both high performance and data redundancy, RAID 10 offers an optimal solution.
- Implement RAID 5 or RAID 6 for General-Purpose Applications: For general-purpose applications where data redundancy is important but performance is not a primary concern, RAID 5 or RAID 6 are suitable choices.
- Consider using a Storage Area Network (SAN): For large-scale deployments or complex storage requirements, a SAN can provide centralized storage management and advanced RAID capabilities.
Benefits of Using RAID in Windows Server
- Enhanced Data Availability: RAID ensures data availability even in the event of drive failures, minimizing downtime and potential business disruptions.
- Improved Performance: RAID configurations can significantly improve I/O performance, leading to faster application response times and increased productivity.
- Increased Storage Capacity: Some RAID levels allow for the creation of larger logical storage volumes than the sum of the individual physical drive capacities, providing greater storage capacity.
- Reduced Risk of Data Loss: RAID provides a robust layer of data protection, minimizing the risk of data loss due to drive failures.
- Simplified Storage Management: RAID simplifies storage management by presenting multiple physical drives as a single logical unit, making it easier to manage and administer.
FAQs about RAID in Windows Server
Q: What is the best RAID level for a file server?
A: The best RAID level for a file server depends on the specific requirements of the server. If data integrity is paramount, RAID 1 or RAID 10 are suitable choices. If performance is a priority, RAID 5 or RAID 6 can provide a balance between redundancy and speed.
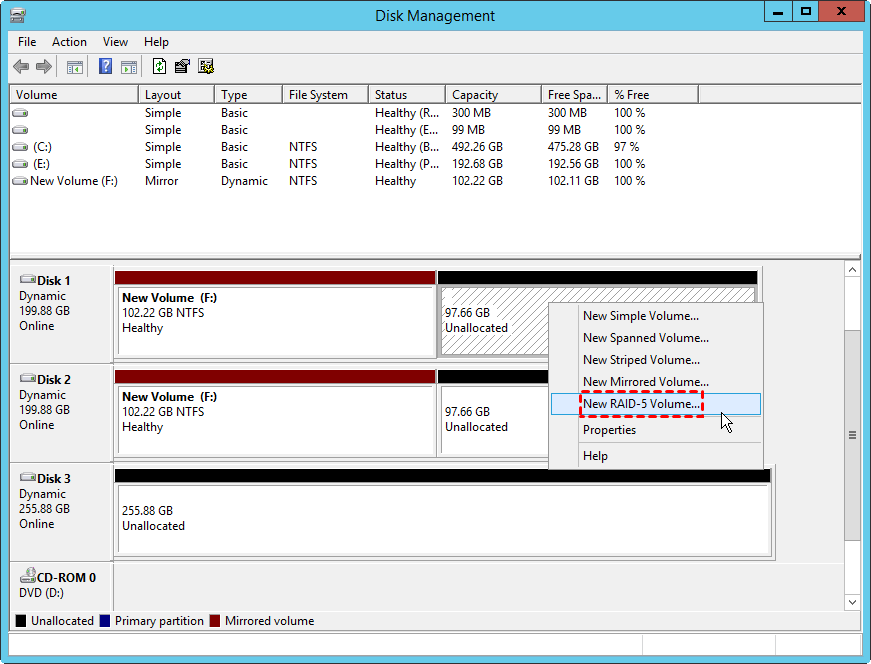
Q: Can I create a RAID configuration using software-based RAID in Windows Server?
A: Yes, Windows Server offers software-based RAID solutions, but they are generally less performant and reliable compared to hardware-based RAID controllers.
Q: What are the disadvantages of using RAID?
A: RAID configurations can be complex to set up and manage, and they can be expensive, especially for higher RAID levels. Additionally, RAID does not protect against all data loss scenarios, such as accidental deletion or malware attacks.
Q: How do I monitor the health of my RAID configuration in Windows Server?
A: You can use tools provided by your RAID controller or Windows Server to monitor the health of your RAID configuration. These tools often provide information about drive status, performance metrics, and potential issues.
Tips for Optimizing RAID Performance
- Use High-Performance Drives: Choose high-performance hard drives, such as SSDs, to maximize RAID performance.
- Optimize Drive Configuration: Ensure that your drives are properly configured for optimal RAID performance.
- Use a Dedicated RAID Controller: A dedicated RAID controller can significantly improve performance compared to software-based RAID solutions.
- Minimize RAID Array Size: Smaller RAID arrays tend to perform better than larger arrays.
- Avoid RAID 0 for Critical Data: RAID 0 offers the highest performance but no data redundancy. It should not be used for critical data.
Conclusion
Implementing RAID in Windows Server is crucial for ensuring data security, performance, and availability. By understanding the different RAID levels and best practices for implementation, organizations can optimize their storage infrastructure for maximum reliability and efficiency. Regularly monitoring RAID performance and health, using high-quality drives, and considering RAID 10 for critical applications are essential strategies for maximizing the benefits of RAID technology in Windows Server environments.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Data Security and Performance Enhancement: A Comprehensive Guide to RAID Configurations in Windows Server. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!