Enabling IIS On Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Enabling IIS on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Enabling IIS on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Enabling IIS on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Enabling IIS on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Windows Server, with its robust features and comprehensive security, is a cornerstone of many organizations’ IT infrastructure. Among its many functionalities, the Internet Information Services (IIS) plays a crucial role in hosting websites, web applications, and services. This article will guide you through the process of enabling IIS on a Windows Server, exploring its importance, benefits, and best practices.
Understanding IIS and its Importance
IIS is a powerful web server platform developed by Microsoft. It allows users to host and manage websites, web applications, and other internet-facing services. IIS is renowned for its flexibility, scalability, and integration with other Microsoft technologies, making it a popular choice for both small businesses and large enterprises.
Key Benefits of Utilizing IIS:
- Website Hosting: IIS provides a robust platform for hosting static and dynamic websites, including content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla.
- Web Application Deployment: IIS enables the deployment and management of web applications, such as ASP.NET applications, PHP applications, and Node.js applications.
- Web Services: IIS can be used to host web services, allowing applications to communicate and exchange data over the internet.
- FTP Server: IIS includes an integrated FTP server, allowing users to securely transfer files between computers.
- Security Features: IIS incorporates robust security features, including authentication, authorization, and encryption, to protect websites and web applications from unauthorized access.
- Integration with Windows Server: IIS seamlessly integrates with other Windows Server technologies, such as Active Directory, SQL Server, and Windows PowerShell, simplifying administration and management.
Enabling IIS on Windows Server: A Step-by-Step Guide
Enabling IIS on Windows Server is a straightforward process. Here’s a detailed guide:
-
Open Server Manager: Navigate to the Windows Server Start Menu and select "Server Manager."
-
Access Server Roles: In the Server Manager dashboard, click on "Manage," and then select "Add Roles and Features."
-
Select Role-Based or Feature-Based Installation: Choose "Role-based or feature-based installation" and click "Next."
-
Select Server: Select the server where you wish to install IIS and click "Next."
-
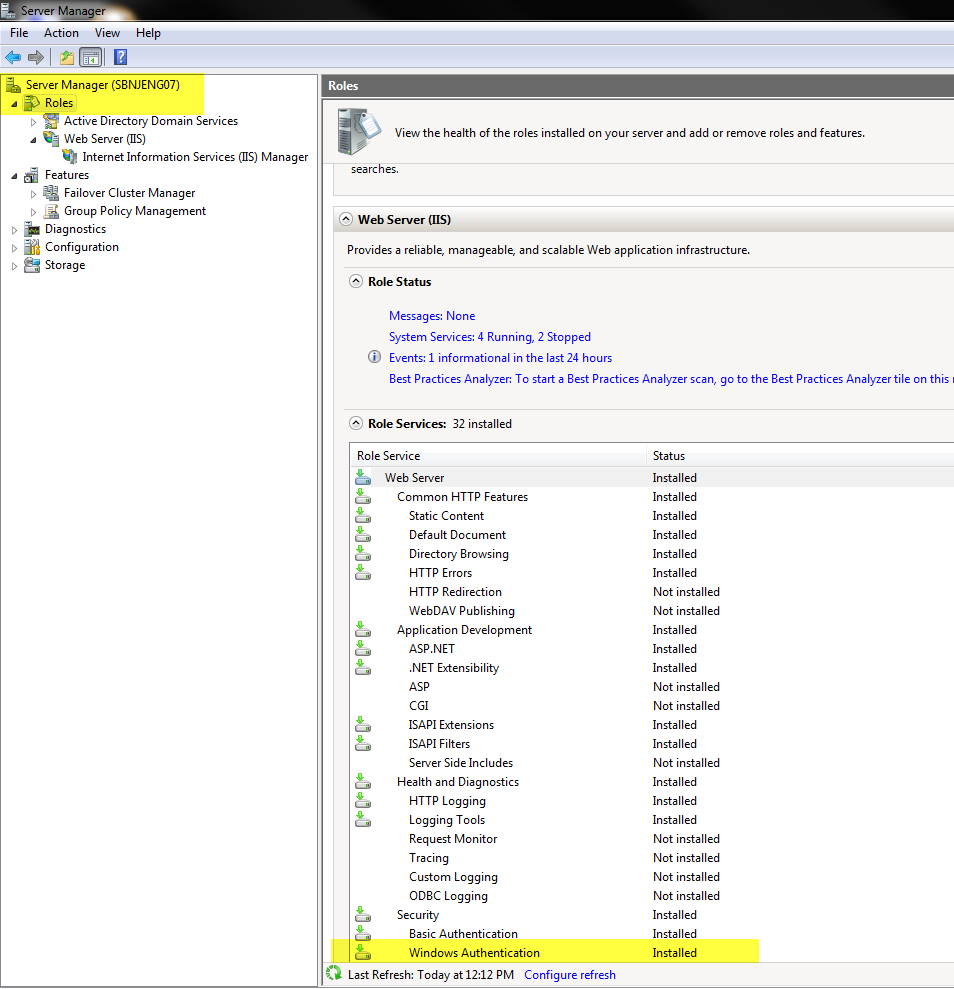
Select Server Roles: On the "Server Roles" page, select "Web Server (IIS)" and click "Next."
-
Select Features: The "Features" page allows you to choose specific IIS features. Select the features you need, such as "ASP.NET," "FTP Server," or "WebDAV Publishing." Click "Next."
-
Confirm Installation: Review your selections and click "Install" to begin the installation process.
-
Complete Installation: Once the installation is complete, IIS will be enabled on your server.
Configuring IIS for Optimal Performance
Once IIS is installed, you can configure it to meet your specific requirements. Here are some essential configuration steps:
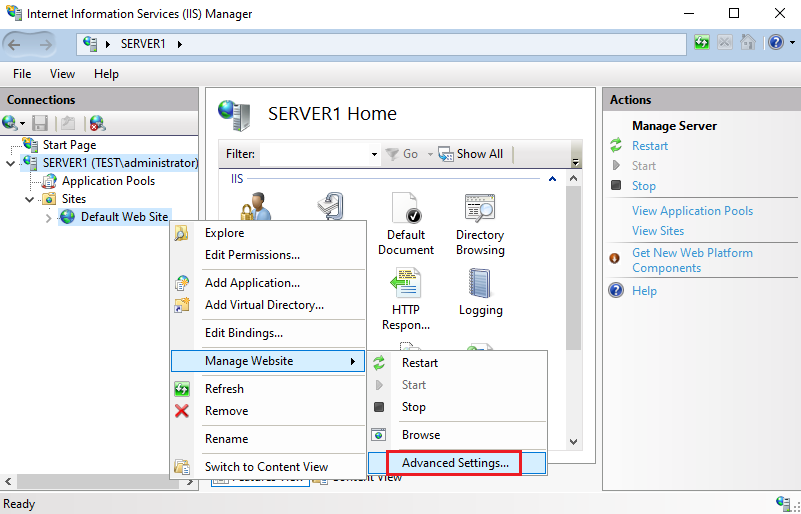
- Website Creation: Create a new website in IIS Manager by right-clicking on "Sites" and selecting "Add Website." Provide a site name, physical path, and binding (e.g., port number and host header).
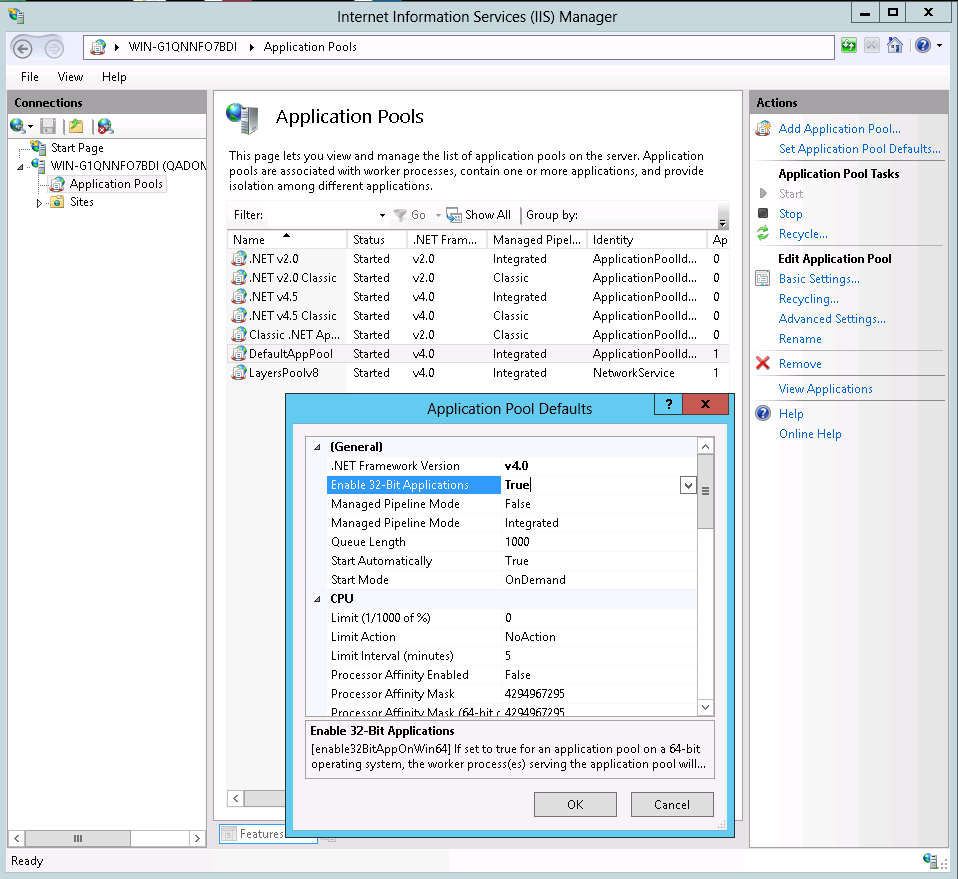
- Application Pools: Configure application pools to isolate websites and web applications, ensuring resource allocation and security.
- Security Settings: Configure security settings, such as authentication methods, authorization rules, and SSL certificates, to protect your websites and applications.
- Performance Tuning: Optimize IIS performance by adjusting settings such as worker process limits, thread counts, and caching options.
Troubleshooting Common IIS Issues
During the installation or configuration process, you may encounter some common issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Firewall Configuration: Ensure that the firewall on your server allows access to the ports used by IIS (e.g., port 80 for HTTP and port 443 for HTTPS).
- Application Pool Identity: Verify that the application pool identity has sufficient permissions to access the necessary files and resources.
- Log Files: Review IIS log files for error messages that can help identify the root cause of the issue.
- IIS Manager: Utilize IIS Manager to diagnose and resolve issues by checking the health of the server, websites, and application pools.
FAQs on Enabling IIS on Windows Server
Q: Can I enable IIS on a Windows Server without installing the full operating system?
A: No, IIS is an integral part of the Windows Server operating system and requires a full installation.
Q: What are the minimum system requirements for running IIS?
A: The system requirements for IIS vary depending on the version and workload. Refer to the official Microsoft documentation for specific requirements.
Q: How can I access IIS Manager?
A: IIS Manager can be accessed by searching for "IIS Manager" in the Windows Server Start Menu.
Q: Is it possible to install multiple versions of IIS on the same server?
A: No, only one version of IIS can be installed on a server at a time.
Q: Can I use IIS to host both websites and web applications?
A: Yes, IIS can be used to host both static websites and dynamic web applications.
Tips for Optimizing IIS Performance
- Regular Updates: Keep IIS and the underlying operating system updated with the latest security patches and performance improvements.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate sufficient resources (e.g., CPU, memory, and disk space) to IIS based on the workload.
- Caching: Utilize caching mechanisms to reduce server load and improve response times.
- Compression: Enable compression to reduce the size of web pages and improve delivery speeds.
- Load Balancing: Implement load balancing to distribute traffic across multiple servers, improving scalability and availability.
Conclusion
Enabling IIS on Windows Server provides a robust platform for hosting websites, web applications, and other internet-facing services. By understanding its importance, benefits, and configuration options, you can leverage IIS to effectively manage your web presence, enhance your online services, and cater to your organization’s growing digital needs. Remember to prioritize security, performance optimization, and regular updates to ensure the smooth operation and reliability of your IIS environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Enabling IIS on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!