Optimizing Network Efficiency: Best Practices For Windows Server 2022 DHCP
Optimizing Network Efficiency: Best Practices for Windows Server 2022 DHCP
Related Articles: Optimizing Network Efficiency: Best Practices for Windows Server 2022 DHCP
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Optimizing Network Efficiency: Best Practices for Windows Server 2022 DHCP. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Optimizing Network Efficiency: Best Practices for Windows Server 2022 DHCP
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a cornerstone of modern network infrastructure, ensuring seamless IP address allocation and configuration management for devices. In the context of Windows Server 2022, implementing effective DHCP practices is paramount for achieving optimal network performance, scalability, and security. This article delves into the key considerations and best practices for managing DHCP services on Windows Server 2022, emphasizing their impact on network efficiency and reliability.
Understanding DHCP: A Foundation for Network Management
DHCP simplifies network administration by automating the process of assigning IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS server addresses to network devices. Instead of manually configuring each device, DHCP servers dynamically allocate these essential network parameters, eliminating the need for manual intervention and reducing the potential for configuration errors.
Core Principles for Efficient DHCP Management
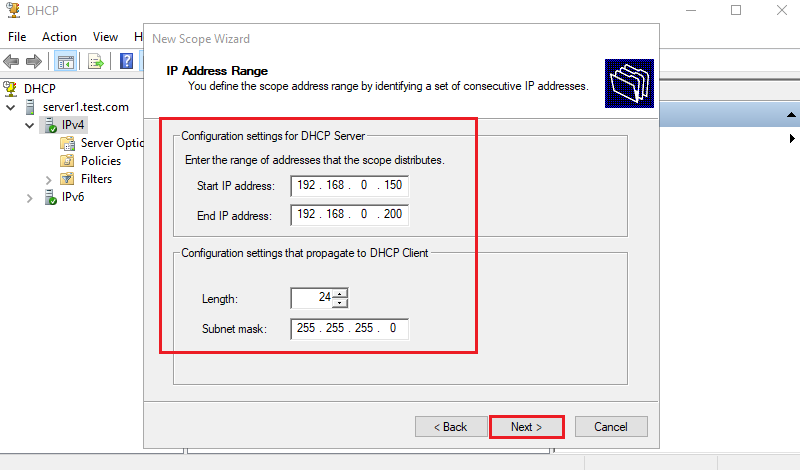
1. Scope Management: Defining Network Boundaries
- Purpose: Scope management allows for the logical grouping of IP addresses based on network segments or specific device types. This enables efficient allocation of IP addresses within defined boundaries, preventing address conflicts and ensuring consistent configuration across different network segments.
-
Best Practices:
- Create Separate Scopes: Define distinct scopes for different network segments, such as separate scopes for wired and wireless networks, different departments, or specific VLANs.
- Utilize Subnets: Assign unique subnets to each scope, ensuring proper address space segmentation and isolation.
- Consider Network Growth: Allocate sufficient IP addresses within each scope to accommodate future network expansion.
2. Reservation and Exclusion: Controlling Address Allocation
- Purpose: Reservations and exclusions provide granular control over IP address allocation. Reservations guarantee specific IP addresses to critical devices, ensuring their consistent connectivity, while exclusions prevent specific IP addresses from being assigned, reserving them for statically configured devices or specific purposes.
-
Best Practices:
- Reserve Addresses for Critical Devices: Reserve IP addresses for servers, routers, firewalls, and other critical network infrastructure, ensuring their consistent availability.
- Exclude Unused Addresses: Exclude IP addresses that are not in use, reducing the potential for address conflicts and enhancing network security.
- Utilize MAC Address Filtering: Implement MAC address filtering in conjunction with reservations to ensure that only authorized devices can obtain specific IP addresses.
3. Lease Duration: Balancing Efficiency and Flexibility
- Purpose: Lease duration determines the period for which a DHCP client can use a specific IP address before it needs to renew the lease.
-
Best Practices:
- Balance Efficiency and Flexibility: Choose a lease duration that balances network efficiency with flexibility. Shorter lease durations improve network responsiveness to changes but increase network traffic. Longer lease durations reduce network traffic but can limit flexibility.
- Consider Network Dynamics: Adjust lease durations based on network dynamics. For highly dynamic environments with frequent device connections and disconnections, shorter lease durations might be more appropriate.
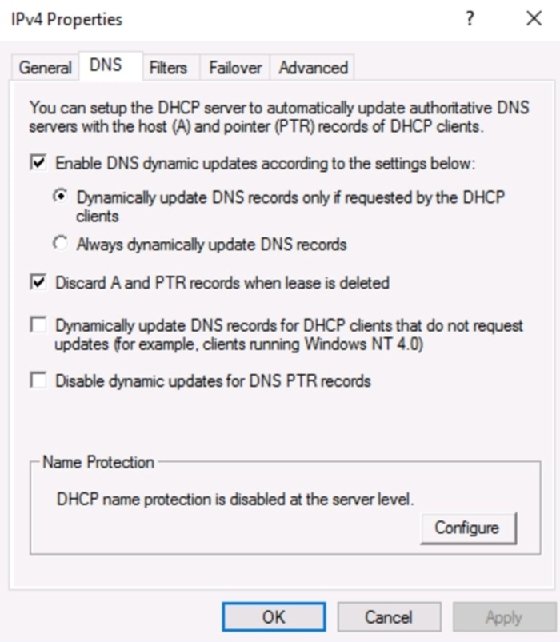
4. Option Management: Configuring Network Services
- Purpose: DHCP options allow for the distribution of additional network configuration parameters beyond basic IP address information. These options can configure DNS servers, WINS servers, boot server addresses, and other network services.
-
Best Practices:
- Configure Essential Options: Configure essential options, such as DNS server addresses, WINS server addresses, and default gateways, to ensure proper network functionality.
- Utilize Custom Options: Leverage custom options to distribute specific configurations to devices based on their type or role.
- Monitor Option Usage: Regularly monitor option usage to ensure that all necessary options are being configured and distributed correctly.
5. Security and Access Control: Protecting the DHCP Service
- Purpose: Securing the DHCP service is crucial for preventing unauthorized access and configuration changes.
-
Best Practices:
- Restrict Access: Configure access control lists (ACLs) to restrict access to the DHCP server to authorized administrators.
- Utilize Strong Authentication: Implement strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, to prevent unauthorized access to the DHCP server.
- Monitor and Audit Changes: Regularly monitor and audit DHCP server configuration changes to identify and address potential security threats.
6. Redundancy and Failover: Ensuring Continuous Availability
- Purpose: Implementing DHCP redundancy and failover mechanisms ensures continuous IP address allocation and configuration management, even in the event of server failure.
-
Best Practices:
- Configure DHCP Failover: Implement DHCP failover by deploying multiple DHCP servers and configuring them to share the DHCP role.
- Utilize Redundant Hardware: Ensure that DHCP servers are deployed on redundant hardware, such as clustered servers or high-availability platforms, to minimize the risk of server failure.
- Test Failover Mechanisms: Regularly test failover mechanisms to ensure that they are functioning correctly and that the DHCP service remains available during server failures.
7. Monitoring and Auditing: Maintaining Optimal Performance
- Purpose: Monitoring and auditing DHCP server activity is essential for identifying potential problems, optimizing performance, and ensuring security.
-
Best Practices:
- Monitor DHCP Server Performance: Regularly monitor DHCP server performance metrics, such as DHCP request rates, lease allocation times, and error rates.
- Audit DHCP Server Configuration: Regularly audit DHCP server configuration changes to identify unauthorized modifications or potential security vulnerabilities.
- Analyze DHCP Logs: Analyze DHCP server logs to identify potential issues, security events, and trends in DHCP request patterns.
Benefits of Effective DHCP Management
- Enhanced Network Performance: Optimized DHCP configuration minimizes IP address allocation delays, reducing network latency and improving overall network performance.
- Improved Network Scalability: Effective DHCP management enables seamless network expansion by providing a flexible and scalable mechanism for IP address allocation.
- Increased Network Security: Secure DHCP configuration prevents unauthorized access and configuration changes, enhancing network security and protecting sensitive data.
- Simplified Network Administration: Automating IP address allocation and configuration management reduces administrative overhead and simplifies network management tasks.
FAQs: Addressing Common DHCP Challenges
1. How can I troubleshoot DHCP issues?
- Check DHCP Server Configuration: Verify that the DHCP server is configured correctly, including scope definitions, reservations, and exclusions.
- Inspect DHCP Logs: Analyze DHCP server logs for error messages, failed lease requests, and other potential issues.
- Verify Network Connectivity: Ensure that the DHCP server is reachable by clients and that network connectivity is functioning correctly.
- Use Network Monitoring Tools: Utilize network monitoring tools to analyze network traffic and identify potential DHCP-related issues.
2. What are the best practices for securing DHCP services?
- Restrict Access to the DHCP Server: Configure access control lists (ACLs) to limit access to the DHCP server to authorized administrators.
- Implement Strong Authentication: Utilize strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, to prevent unauthorized access to the DHCP server.
- Monitor DHCP Server Activity: Regularly monitor DHCP server activity for suspicious or unusual activity.
- Audit DHCP Server Configuration: Regularly audit DHCP server configuration changes to identify and address potential security threats.
3. How can I optimize DHCP performance?
- Utilize Scope Management: Define distinct scopes for different network segments to optimize IP address allocation.
- Configure Lease Duration Appropriately: Choose a lease duration that balances network efficiency with flexibility.
- Implement DHCP Failover: Configure DHCP failover to ensure continuous IP address allocation in the event of server failure.
- Monitor DHCP Server Performance: Regularly monitor DHCP server performance metrics to identify and address potential performance bottlenecks.
Tips for Effective DHCP Management
- Document DHCP Configuration: Maintain detailed documentation of DHCP server configuration, including scopes, reservations, exclusions, and options.
- Regularly Back Up DHCP Configuration: Regularly back up DHCP server configuration to prevent data loss in the event of server failure.
- Utilize DHCP Management Tools: Utilize DHCP management tools to simplify DHCP configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting tasks.
- Stay Updated on DHCP Best Practices: Stay informed about the latest DHCP best practices and security recommendations.
Conclusion: Maximizing Network Efficiency with Best Practices
Implementing best practices for DHCP management in Windows Server 2022 is crucial for optimizing network efficiency, scalability, and security. By carefully defining scopes, managing reservations and exclusions, configuring lease durations, securing the DHCP service, and implementing redundancy and failover mechanisms, organizations can ensure seamless IP address allocation, minimize network downtime, and enhance overall network performance. Regular monitoring, auditing, and adherence to industry best practices further contribute to a robust and reliable network infrastructure.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Optimizing Network Efficiency: Best Practices for Windows Server 2022 DHCP. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!