The End Of An Era: Understanding The Implications Of Windows Server 2026’s Lifecycle
The End of an Era: Understanding the Implications of Windows Server 2026’s Lifecycle
Related Articles: The End of an Era: Understanding the Implications of Windows Server 2026’s Lifecycle
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The End of an Era: Understanding the Implications of Windows Server 2026’s Lifecycle. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The End of an Era: Understanding the Implications of Windows Server 2026’s Lifecycle
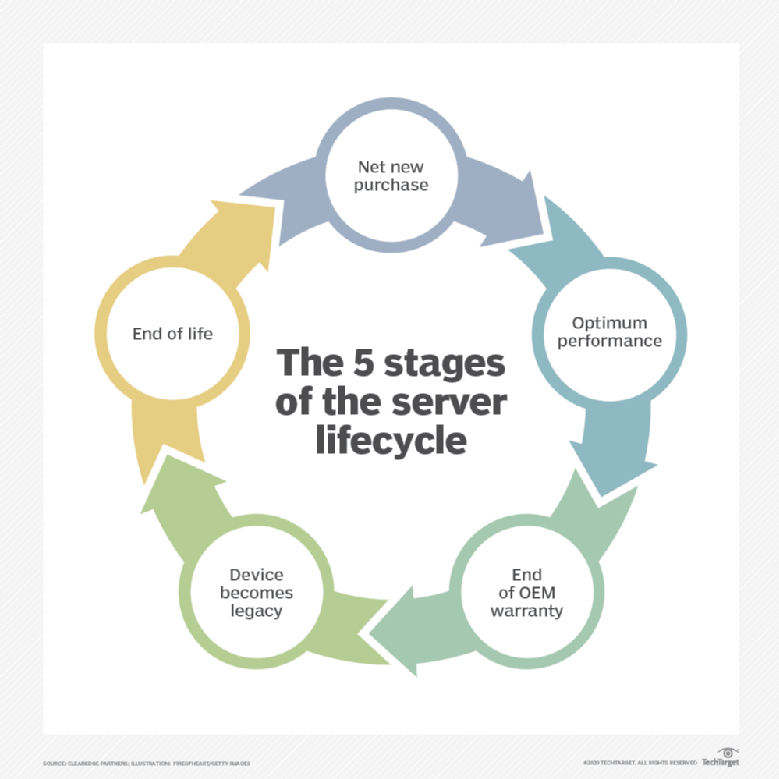
While the concept of "Windows Server 2026" doesn’t currently exist in Microsoft’s product roadmap, the hypothetical scenario of its end of life presents a valuable opportunity to explore the broader implications of technology lifecycles and the importance of proactive planning.
The end of life for any operating system, particularly a server operating system, signifies a critical juncture for organizations. It marks the cessation of Microsoft’s support, including security updates, bug fixes, and technical assistance. This means organizations running such systems are left vulnerable to potential security threats, performance issues, and compatibility problems.
The Importance of Understanding End-of-Life Dates:
- Security Vulnerabilities: After the end of life, Microsoft ceases to issue security patches. This leaves systems susceptible to previously unknown vulnerabilities, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
- Compliance Risks: Many industries and organizations adhere to stringent compliance regulations that mandate the use of supported software. Failing to upgrade to a supported system could result in non-compliance and potential legal consequences.
- Interoperability Issues: New applications and software are often designed to be compatible with the latest operating systems. Using outdated systems can lead to incompatibility issues, hindering productivity and innovation.
- Support and Maintenance: End-of-life systems often lack vendor support, making troubleshooting and maintenance more challenging. This can lead to downtime, increased costs, and reduced efficiency.
The Transition Process:
Moving away from an end-of-life operating system is a multi-faceted process that requires careful planning and execution. Organizations should consider the following steps:
- Assess the Current Infrastructure: Begin by comprehensively evaluating the existing environment, including applications, hardware, and dependencies. This assessment helps identify potential compatibility issues and plan for necessary upgrades or replacements.
- Define Migration Objectives: Clearly define the goals and objectives for the migration process. This might include improving security, enhancing performance, or achieving greater scalability.
- Choose the Right Migration Strategy: Select the most suitable migration approach, considering factors like budget, timeline, and available resources. Options include in-place upgrades, cloud migration, or a hybrid approach.
- Test and Validate: Thoroughly test the new environment before going live to ensure seamless transition and minimize downtime.
- Implement and Monitor: Execute the migration plan and continuously monitor the new environment to ensure stability and performance.
Addressing Potential Challenges:
The transition process can present challenges, such as:
- Cost: Upgrading infrastructure, acquiring new software licenses, and training staff can be costly.
- Complexity: Migrating complex systems can be intricate and time-consuming, requiring specialized expertise.
- Downtime: Minimizing downtime during the migration process is crucial to maintain business continuity.
- Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between the new environment and existing applications is essential.
FAQs:
1. What happens after the end of life for a server operating system?
After the end of life, Microsoft will no longer provide security updates, bug fixes, or technical support for the operating system. This leaves organizations vulnerable to security risks and performance issues.
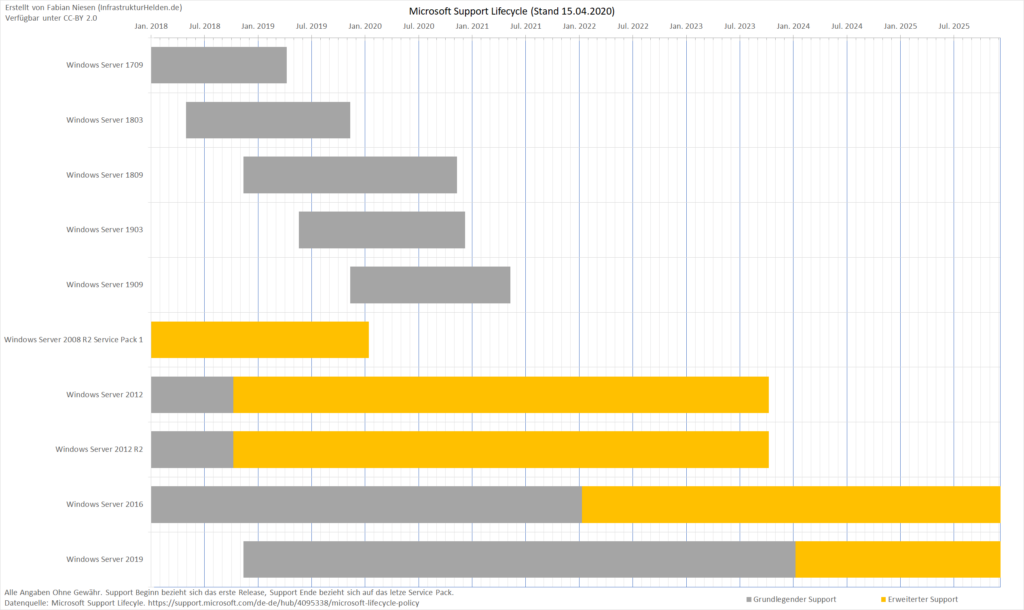
2. How do I know when an operating system reaches its end of life?
Microsoft publishes a lifecycle policy for all its products, including server operating systems. This policy outlines the supported lifespan and end-of-life dates.
3. What are the benefits of upgrading to a supported operating system?
Upgrading to a supported operating system provides enhanced security, improved performance, better compatibility, and ongoing support from Microsoft.
4. How long does it take to migrate to a new operating system?
The time required for migration depends on factors such as the size and complexity of the environment, the chosen migration approach, and available resources.
5. What are the best practices for migrating to a new operating system?
Best practices include thorough planning, comprehensive testing, and minimizing downtime during the transition.
Tips for Preparing for an End-of-Life Scenario:
- Stay Informed: Monitor Microsoft’s product lifecycle policy and be aware of upcoming end-of-life dates.
- Plan Ahead: Develop a proactive plan for migrating to a supported operating system well in advance of the end-of-life date.
- Assess and Evaluate: Regularly assess your infrastructure and applications to identify potential compatibility issues.
- Prioritize Security: Implement robust security measures to mitigate risks associated with outdated systems.
- Seek Professional Assistance: Consider engaging experienced IT professionals for guidance and support during the migration process.
Conclusion:
While the concept of "Windows Server 2026" is hypothetical, the underlying principles of technology lifecycles and proactive planning remain paramount. Organizations must recognize the importance of staying informed about end-of-life dates and proactively preparing for transitions. By embracing a well-defined migration strategy, organizations can minimize risks, maintain business continuity, and ensure a smooth transition to a secure and supported environment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The End of an Era: Understanding the Implications of Windows Server 2026’s Lifecycle. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!