The Future Of Network Management: Exploring The Potential Of Software-Defined Networking With Windows Server
The Future of Network Management: Exploring the Potential of Software-Defined Networking with Windows Server
Related Articles: The Future of Network Management: Exploring the Potential of Software-Defined Networking with Windows Server
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Future of Network Management: Exploring the Potential of Software-Defined Networking with Windows Server. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Future of Network Management: Exploring the Potential of Software-Defined Networking with Windows Server
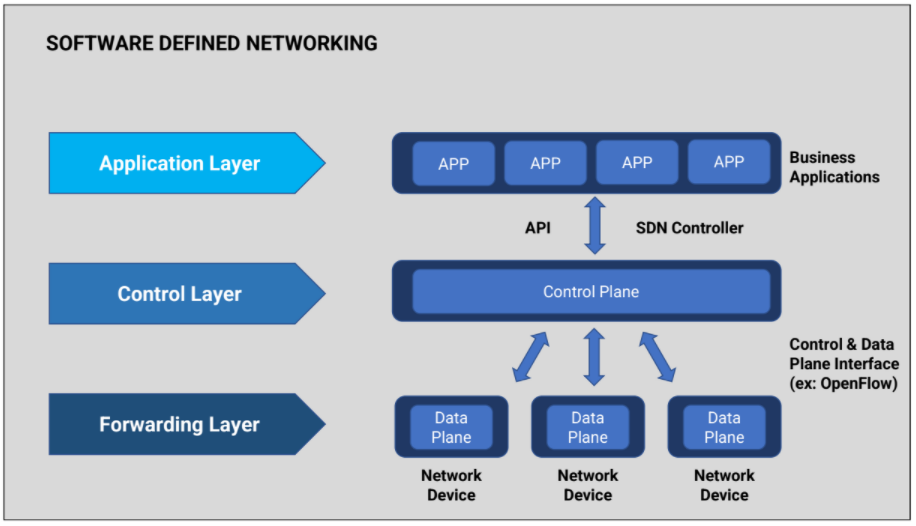
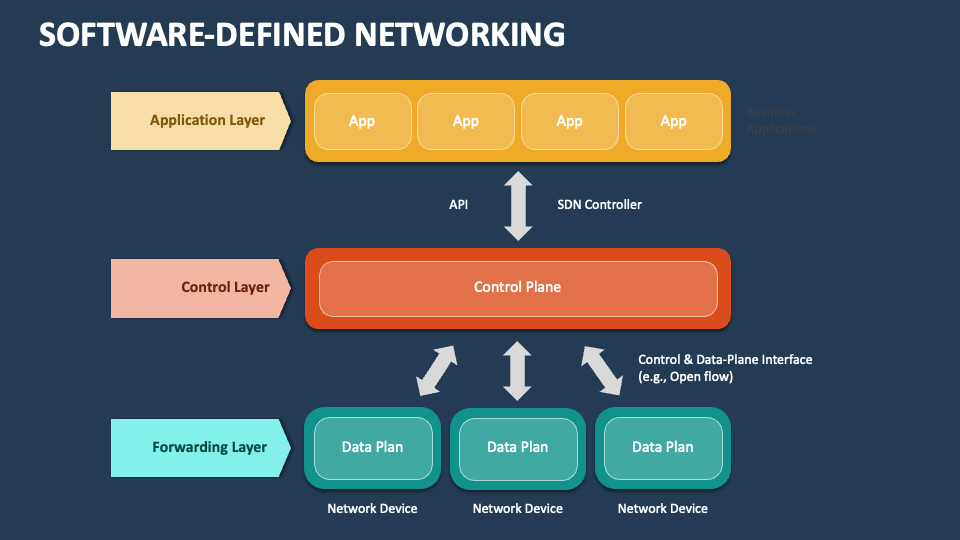
The landscape of network management is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by the increasing complexity of modern IT environments and the ever-growing demands for agility and efficiency. Software-Defined Networking (SDN) has emerged as a powerful paradigm, offering a centralized and programmable approach to network control, enabling organizations to streamline operations, optimize resource utilization, and enhance security. While the concept of SDN is not new, its adoption is gaining momentum, particularly with the advent of platforms like Windows Server, which provide robust and comprehensive SDN capabilities.
Understanding the Essence of Software-Defined Networking
Traditional network management relied heavily on hardware-based solutions, with each network device operating independently and requiring manual configuration. This approach often resulted in cumbersome processes, limited scalability, and difficulty in adapting to changing business needs. SDN, on the other hand, decouples the control plane from the data plane, creating a virtualized network environment where network infrastructure can be managed and configured through software. This separation allows for centralized control, automation, and programmability, empowering organizations to:
- Simplify Network Management: SDN centralizes network configuration and management, reducing the complexity associated with managing multiple devices and configurations. This streamlined approach saves time, effort, and resources, allowing IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Enhance Network Agility: SDN enables rapid deployment and configuration changes, facilitating quick adaptation to evolving business requirements. Organizations can easily scale their networks up or down as needed, ensuring optimal resource utilization and cost-effectiveness.
- Improve Network Security: SDN provides granular control over network traffic, allowing organizations to implement robust security policies and detect and mitigate threats more effectively. Centralized security management simplifies policy enforcement and improves overall network resilience.
- Optimize Network Performance: SDN facilitates real-time monitoring and analysis of network traffic, enabling organizations to identify bottlenecks and optimize network performance. This data-driven approach allows for proactive problem resolution and continuous improvement.
Windows Server: A Powerful Platform for SDN
Windows Server has emerged as a leading platform for implementing SDN solutions, offering a comprehensive suite of features and tools designed to simplify and enhance network management. Here’s a glimpse into the key capabilities of Windows Server in the context of SDN:
- Network Controller: Windows Server provides a centralized network controller, enabling the orchestration and management of virtual networks and physical network devices. This controller acts as the brain of the SDN solution, receiving commands and instructions from applications and translating them into actions on the network infrastructure.
- Virtual Networking: Windows Server supports the creation and management of virtual networks, allowing organizations to isolate and manage different workloads within their IT environment. This virtualization capability facilitates flexibility and scalability, enabling organizations to quickly adapt to changing needs.
- Network Virtualization: Windows Server enables the virtualization of physical network devices, such as routers and switches, through software. This virtualized approach allows for greater flexibility and control, enabling organizations to provision and manage network resources more efficiently.
- Policy-Based Management: Windows Server supports the implementation of policy-based management, enabling organizations to define and enforce network policies across their entire infrastructure. This centralized approach simplifies security management, ensures compliance, and reduces the risk of human error.
- Open Standards and APIs: Windows Server adheres to open standards and APIs, facilitating interoperability with other SDN solutions and enabling seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure. This open approach fosters flexibility and allows organizations to leverage best-of-breed solutions.
Benefits of Implementing SDN with Windows Server
The adoption of SDN with Windows Server offers a multitude of benefits for organizations across various industries:
- Enhanced Network Agility: SDN with Windows Server empowers organizations to rapidly deploy and configure network changes, enabling them to respond swiftly to evolving business demands and seize new opportunities.
- Simplified Network Management: By centralizing network control and automation, SDN with Windows Server reduces the complexity of managing and maintaining network infrastructure, freeing up IT resources for strategic initiatives.
- Improved Network Security: SDN with Windows Server provides granular control over network traffic, enabling organizations to implement robust security policies and mitigate threats more effectively, enhancing overall network resilience.
- Optimized Network Performance: SDN with Windows Server allows for real-time monitoring and analysis of network traffic, enabling organizations to identify and resolve bottlenecks, maximizing network efficiency and user experience.
- Cost Savings: SDN with Windows Server streamlines network operations, reduces the need for specialized hardware, and optimizes resource utilization, leading to significant cost savings for organizations.
FAQs Regarding Windows Server and SDN
Q: What are the prerequisites for implementing SDN with Windows Server?
A: Implementing SDN with Windows Server requires a compatible hardware infrastructure, including servers, switches, and routers that support the necessary protocols and features. Additionally, organizations need to assess their existing IT infrastructure and ensure it meets the requirements for virtualization and network management.
Q: Is SDN with Windows Server suitable for all organizations?
A: SDN with Windows Server is well-suited for organizations of all sizes and across various industries. However, the specific benefits and suitability of SDN depend on the organization’s network size, complexity, and specific business needs.
Q: How secure is SDN with Windows Server?
A: SDN with Windows Server offers robust security features, including centralized policy management, granular traffic control, and encryption capabilities. However, it’s crucial to implement comprehensive security best practices, such as regular security updates, strong passwords, and multi-factor authentication, to further enhance network security.
Q: What are the challenges associated with implementing SDN with Windows Server?
A: Implementing SDN with Windows Server can present certain challenges, such as the need for skilled personnel, potential compatibility issues with legacy systems, and the complexity of managing a large-scale virtualized network environment. However, these challenges can be mitigated through careful planning, training, and the use of appropriate tools and resources.
Tips for Successful SDN Implementation with Windows Server
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot project to test the feasibility of SDN with Windows Server in a controlled environment before scaling it to the entire network.
- Plan Carefully: Develop a comprehensive implementation plan that outlines the goals, scope, timeline, and resources required for successful deployment.
- Train Your Team: Ensure your IT team has the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively manage and maintain an SDN environment.
- Choose the Right Hardware: Select compatible hardware infrastructure that meets the performance and scalability requirements of your SDN solution.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor network performance and optimize the SDN configuration to ensure optimal performance and security.
Conclusion
The adoption of Software-Defined Networking with Windows Server represents a significant shift in network management, offering a powerful and flexible approach to optimize network performance, enhance security, and streamline operations. While challenges exist, the benefits of SDN far outweigh the drawbacks, enabling organizations to achieve greater agility, efficiency, and cost savings. As technology continues to evolve, Windows Server’s role in SDN is expected to grow, further empowering organizations to navigate the ever-changing landscape of network management and unlock the full potential of their IT infrastructure.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Future of Network Management: Exploring the Potential of Software-Defined Networking with Windows Server. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!