Understanding And Configuring Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding and Configuring Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding and Configuring Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Configuring Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding and Configuring Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding and Configuring Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Foundation: Windows Server Editions
- 3.2 Core Features of Windows Server
- 3.3 Configuring Windows Server: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.4 Benefits of Windows Server
- 3.5 FAQs about Windows Server
- 3.6 Tips for Managing Windows Server
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding and Configuring Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
The evolution of technology necessitates a constant adaptation to new systems and software. In the realm of server operating systems, Microsoft’s Windows Server has consistently been a dominant force, offering robust features and reliable performance. As organizations navigate the complexities of modern technology, understanding the intricacies of Windows Server becomes paramount. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a deep dive into the world of Windows Server, exploring its key features, configuration processes, and the benefits it offers to businesses of all sizes.
The Foundation: Windows Server Editions
Windows Server comes in several editions, each tailored to specific needs and environments. Understanding the differences between these editions is crucial for selecting the most suitable option for your organization.
- Windows Server Essentials: Designed for small businesses, this edition provides a streamlined experience with integrated features for file sharing, email, and remote access.
- Windows Server Standard: A versatile edition suitable for a wide range of scenarios, including file and print services, web hosting, and virtualization.
- Windows Server Datacenter: This edition is designed for large enterprises and high-performance computing environments, offering advanced features such as virtualization, scalability, and high availability.
Core Features of Windows Server
Windows Server offers a comprehensive suite of features that enable businesses to manage their IT infrastructure effectively. Some key features include:
- Active Directory: A directory service that manages users, groups, computers, and other network resources. It facilitates user authentication, access control, and centralized administration.
- Hyper-V: A powerful virtualization platform that allows you to run multiple operating systems on a single physical server. This enables efficient resource utilization and reduces hardware costs.
- Server Manager: A centralized management console that provides a unified interface for managing all aspects of your server environment, including roles, features, and updates.
- File and Print Services: Enables sharing files and printers across the network, simplifying collaboration and streamlining workflows.
- Remote Desktop Services: Allows remote access to your server and applications, enabling users to work from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Internet Information Services (IIS): A web server platform that enables hosting websites, applications, and web services.
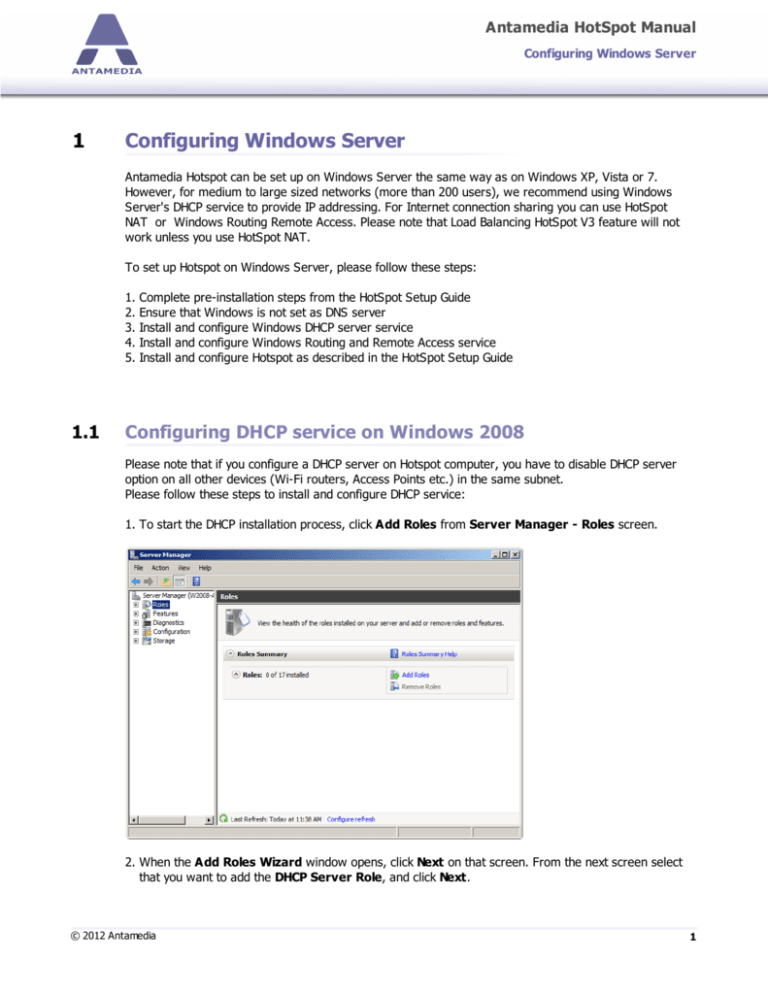
Configuring Windows Server: A Step-by-Step Guide
Setting up Windows Server involves several steps, each crucial for ensuring a secure and efficient environment.
1. Installation:
- Hardware Requirements: Ensure your hardware meets the minimum system requirements for your chosen Windows Server edition.
- Installation Media: Obtain the installation media, either a DVD or a downloadable ISO file.
- Boot from Media: Start the installation process by booting from the installation media.
- License Key: Enter your valid Windows Server license key during installation.
- Customization: Configure basic settings such as language, time zone, and network settings.
2. Server Manager:
- Initial Configuration: After installation, Server Manager will guide you through the initial configuration process.
- Roles and Features: Install the necessary roles and features based on your server’s intended purpose. For example, installing the "Active Directory Domain Services" role enables you to create a domain controller.
- Updates: Keep your server up-to-date by installing the latest security patches and updates.
3. Active Directory:
- Domain Creation: If you are setting up a domain controller, create a new domain and configure its settings.
- User and Group Management: Create user accounts, assign permissions, and manage groups to control access to resources.
- DNS Integration: Integrate Active Directory with Domain Name System (DNS) to resolve hostnames and facilitate communication within your network.
4. Hyper-V:
- Virtual Machine Creation: Create virtual machines (VMs) to host other operating systems and applications.
- Resource Allocation: Configure resource allocation for each VM, such as CPU, memory, and storage space.
- Network Configuration: Connect VMs to the network and configure network settings.
5. File and Print Services:
- Share Folders: Create shared folders and define access permissions to allow users to access files and printers.
- Printer Management: Install and manage printers, enabling users to print from their workstations.
6. Remote Desktop Services:
- Remote Desktop Access: Enable remote desktop access to your server, allowing users to connect remotely.
- Remote Desktop Gateway: Set up a remote desktop gateway to provide secure remote access from outside the corporate network.
7. Security Best Practices:
- Strong Passwords: Enforce strong password policies for all user accounts.
- Regular Updates: Install security patches and updates regularly to protect your server from vulnerabilities.
- Firewall Configuration: Configure the firewall to block unauthorized access to your server.
- Antivirus Software: Install and maintain antivirus software to protect against malware.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Implement auditing and monitoring tools to track user activity and detect suspicious behavior.
Benefits of Windows Server
Implementing Windows Server brings a multitude of benefits to organizations, enhancing their operational efficiency and security posture.
- Centralized Management: Server Manager provides a unified platform for managing all aspects of your server environment, streamlining administration and reducing complexity.
- Enhanced Security: Active Directory and other built-in security features provide robust protection against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Increased Productivity: File and print services facilitate collaboration and streamline workflows, boosting overall productivity.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Windows Server offers scalable solutions that can adapt to growing business needs, ensuring smooth transitions and avoiding performance bottlenecks.
- Cost Savings: Virtualization technologies such as Hyper-V enable efficient resource utilization, reducing hardware costs and energy consumption.
- Improved Reliability: Windows Server is designed for high availability and reliability, ensuring continuous operation and minimizing downtime.
FAQs about Windows Server
Q: What are the minimum hardware requirements for Windows Server?
A: The hardware requirements vary depending on the chosen edition and intended usage. It is recommended to consult the official Microsoft documentation for specific system requirements.
Q: How do I create a new user account in Active Directory?
A: You can create new user accounts in Active Directory using the "Active Directory Users and Computers" console. This involves specifying the user’s name, password, and other relevant details.
Q: How do I install a new role or feature on my Windows Server?
A: You can install new roles and features using Server Manager. Navigate to "Add Roles and Features" and select the desired roles and features based on your server’s intended purpose.
Q: What are the different types of Windows Server licenses?
A: Windows Server licenses come in various forms, including per-processor licenses, per-core licenses, and per-user licenses. The specific licensing model depends on the chosen edition and the server’s usage.
Q: How do I troubleshoot common Windows Server issues?
A: Troubleshooting Windows Server issues can involve various methods, including checking event logs, running diagnostic tools, and consulting Microsoft documentation. It is often helpful to seek assistance from a qualified IT professional.
Tips for Managing Windows Server
- Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance tasks such as system updates, disk cleanup, and security scans to ensure optimal performance and security.
- Backup Strategy: Implement a comprehensive backup strategy to protect your server data from loss or corruption.
- Monitoring Tools: Utilize monitoring tools to track server performance, identify potential issues, and ensure system stability.
- Security Best Practices: Adhere to security best practices such as strong passwords, regular updates, and firewall configuration to protect your server from cyber threats.
- Professional Support: Consider seeking professional support from Microsoft or a certified partner for complex configurations, troubleshooting, and ongoing maintenance.
Conclusion
Windows Server remains a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure, providing a robust platform for managing and securing business networks. By understanding the key features, configuration processes, and benefits of Windows Server, organizations can leverage its capabilities to streamline operations, enhance security, and drive efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest features and best practices for Windows Server is essential for navigating the ever-changing landscape of IT.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Configuring Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
