Understanding And Resolving Slow Remote Desktop Performance In Windows Server Environments
Understanding and Resolving Slow Remote Desktop Performance in Windows Server Environments
Related Articles: Understanding and Resolving Slow Remote Desktop Performance in Windows Server Environments
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Resolving Slow Remote Desktop Performance in Windows Server Environments. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Resolving Slow Remote Desktop Performance in Windows Server Environments
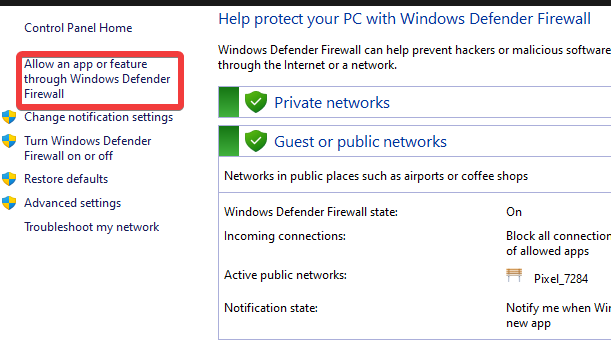
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a cornerstone of modern network administration, enabling remote access and management of servers, workstations, and applications. However, slow RDP performance can significantly hinder productivity and operational efficiency. This article explores the common causes of slow RDP performance in Windows Server environments and provides practical solutions to address these challenges.
Common Causes of Slow RDP Performance:
1. Network Bandwidth and Latency:
- Insufficient Bandwidth: Limited network bandwidth can choke the data transfer necessary for smooth RDP sessions. This is particularly noticeable when transferring large files or displaying graphics-intensive applications.
- High Latency: Network latency, the time it takes for data to travel between the client and server, can cause noticeable delays in user interactions. This is often exacerbated by long distances, congested network paths, or unreliable network connections.
2. Server Resource Constraints:
- CPU Bottlenecks: A heavily loaded CPU can struggle to handle the processing demands of an RDP session, leading to sluggish performance.
- Memory Limitations: Insufficient RAM can result in excessive disk swapping, further impacting RDP responsiveness.
- Disk I/O Bottlenecks: Slow disk performance can hinder the loading of applications and files required for RDP sessions.
3. RDP Client and Server Configuration:
- Incorrect Settings: Improperly configured RDP settings, such as low color depths, low frame rates, or excessive compression, can degrade visual quality and responsiveness.
- Outdated Software: Outdated RDP clients or server software may lack the latest performance optimizations and security enhancements.
4. Security Measures:
- Firewall Restrictions: Overly restrictive firewalls can block necessary network traffic, impacting RDP connectivity.
- Antivirus Software: Aggressive antivirus software can scan RDP traffic, potentially introducing delays.
5. User Interface Elements:
- Excessive Desktop Items: A cluttered desktop with numerous icons and applications can slow down the initial loading of the RDP session.
- High-Resolution Displays: RDP sessions on high-resolution displays may require more processing power and bandwidth, potentially leading to performance degradation.
Troubleshooting and Resolution Strategies:
1. Network Optimization:
- Increase Bandwidth: Evaluate the available bandwidth and consider upgrading the network infrastructure if necessary.
- Reduce Latency: Optimize network paths, minimize network hops, and prioritize RDP traffic.
- Network Monitoring: Utilize network monitoring tools to identify network bottlenecks and potential issues.
2. Server Resource Optimization:
- Monitor Server Performance: Use performance monitoring tools to identify resource constraints, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk I/O.
- Optimize Server Configuration: Adjust server settings, such as reducing the number of active services, increasing available RAM, and optimizing disk configurations.
- Upgrade Server Hardware: Consider upgrading hardware components, such as the CPU, RAM, and storage, if resource limitations persist.
3. RDP Client and Server Configuration:
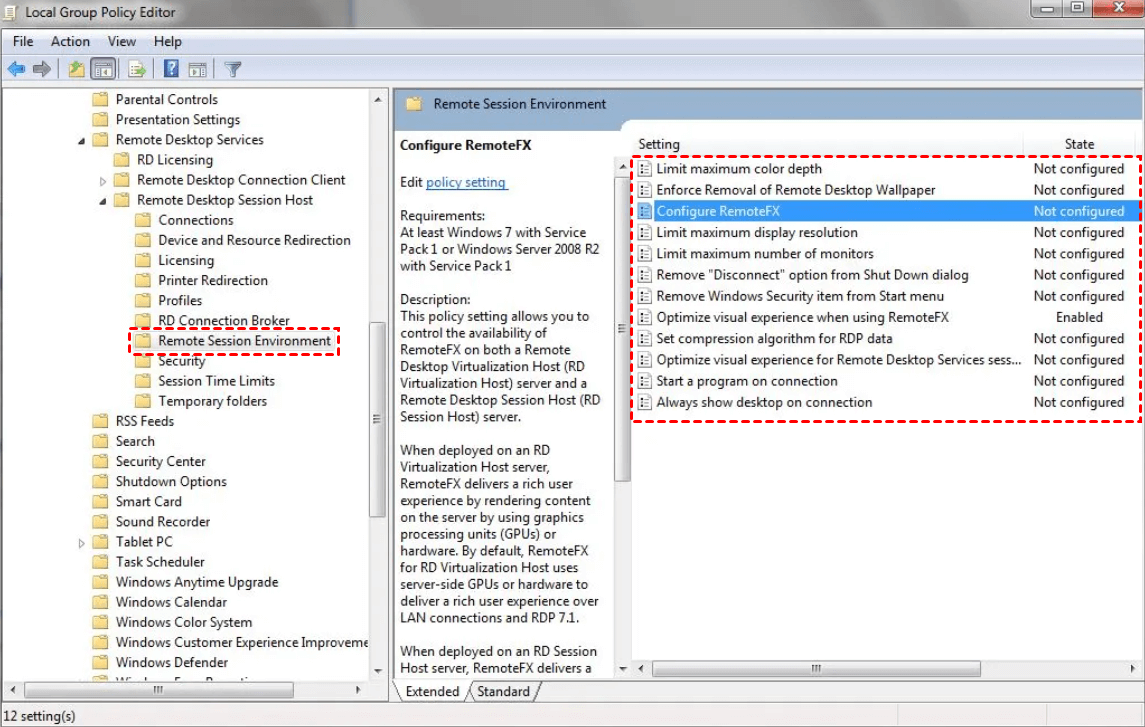
- Configure RDP Settings: Adjust RDP settings to optimize performance, such as increasing color depth, frame rate, and compression levels.
- Update Software: Ensure both the RDP client and server software are up-to-date with the latest security patches and performance enhancements.
- Enable RDP Features: Utilize advanced RDP features, such as the "Enhanced Desktop" mode, which can improve performance and visual fidelity.
4. Security Measures:
- Review Firewall Rules: Ensure that firewall rules allow necessary RDP traffic.
- Optimize Antivirus Settings: Fine-tune antivirus software settings to minimize impact on RDP performance.
5. User Interface Optimization:
- Simplify Desktop: Minimize the number of icons and applications on the desktop.
- Adjust Resolution: Consider using a lower resolution or scaling settings for RDP sessions on high-resolution displays.
FAQs:
Q: What are the most common causes of slow RDP performance?
A: The most common causes include insufficient network bandwidth, high latency, server resource constraints, outdated software, and security measures that impede RDP traffic.
Q: How can I improve RDP performance on a slow network connection?
A: You can try increasing the available bandwidth, optimizing network paths to reduce latency, and prioritizing RDP traffic.
Q: What are some server configuration settings that can impact RDP performance?
A: Server settings that can affect RDP performance include the number of active services, available RAM, and disk configurations.
Q: How can I optimize RDP settings for better performance?
A: Adjust RDP settings to increase color depth, frame rate, and compression levels, and consider enabling advanced features like "Enhanced Desktop" mode.
Q: Is it possible to use a VPN to improve RDP performance?
A: A VPN can sometimes improve RDP performance by providing a more secure and dedicated network connection, but it can also introduce additional latency.
Tips:
- Regularly monitor server performance and network traffic.
- Optimize server configurations and RDP settings to match your specific needs.
- Keep both RDP client and server software up-to-date.
- Utilize network monitoring tools to identify and address potential bottlenecks.
Conclusion:
Slow RDP performance can significantly impact productivity and operational efficiency in Windows Server environments. By understanding the common causes of slow RDP performance and implementing appropriate troubleshooting and resolution strategies, administrators can significantly improve the responsiveness and reliability of remote desktop connections. Regular monitoring, optimization, and ongoing maintenance are crucial to ensure optimal performance and minimize disruptions to critical operations.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Resolving Slow Remote Desktop Performance in Windows Server Environments. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!