Understanding The Removal Of IIS On Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Removal of IIS on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Removal of IIS on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Removal of IIS on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Removal of IIS on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide

While Windows Server 2025 is a hypothetical future release, the principles of removing Internet Information Services (IIS) remain consistent across Windows Server versions. This article will provide a detailed understanding of the process, its implications, and best practices.
The Role of IIS in Windows Server
IIS is a crucial component of Windows Server, serving as the foundation for web hosting and web application deployment. It provides a comprehensive platform for handling HTTP requests, managing websites, and enabling various web-related functionalities. However, situations may arise where removing IIS becomes necessary.
Reasons for Removing IIS
Several factors can necessitate the removal of IIS from a Windows Server:
- Security: IIS, like any software, can be a potential vulnerability target. If the server is not actively used for web hosting, removing IIS minimizes the attack surface and enhances overall security.
- Resource Optimization: IIS consumes system resources, especially when handling heavy traffic. If the server is primarily used for other purposes, removing IIS can free up resources for other applications.
- Software Conflicts: In rare cases, IIS might conflict with other software installed on the server. Removing IIS can resolve such conflicts and improve system stability.
- Server Transition: During server migration or decommissioning, removing IIS ensures a clean transition and avoids potential conflicts with the new environment.
The Uninstall Process
The process of removing IIS from a Windows Server is straightforward and can be achieved through the Server Manager interface or the command line.
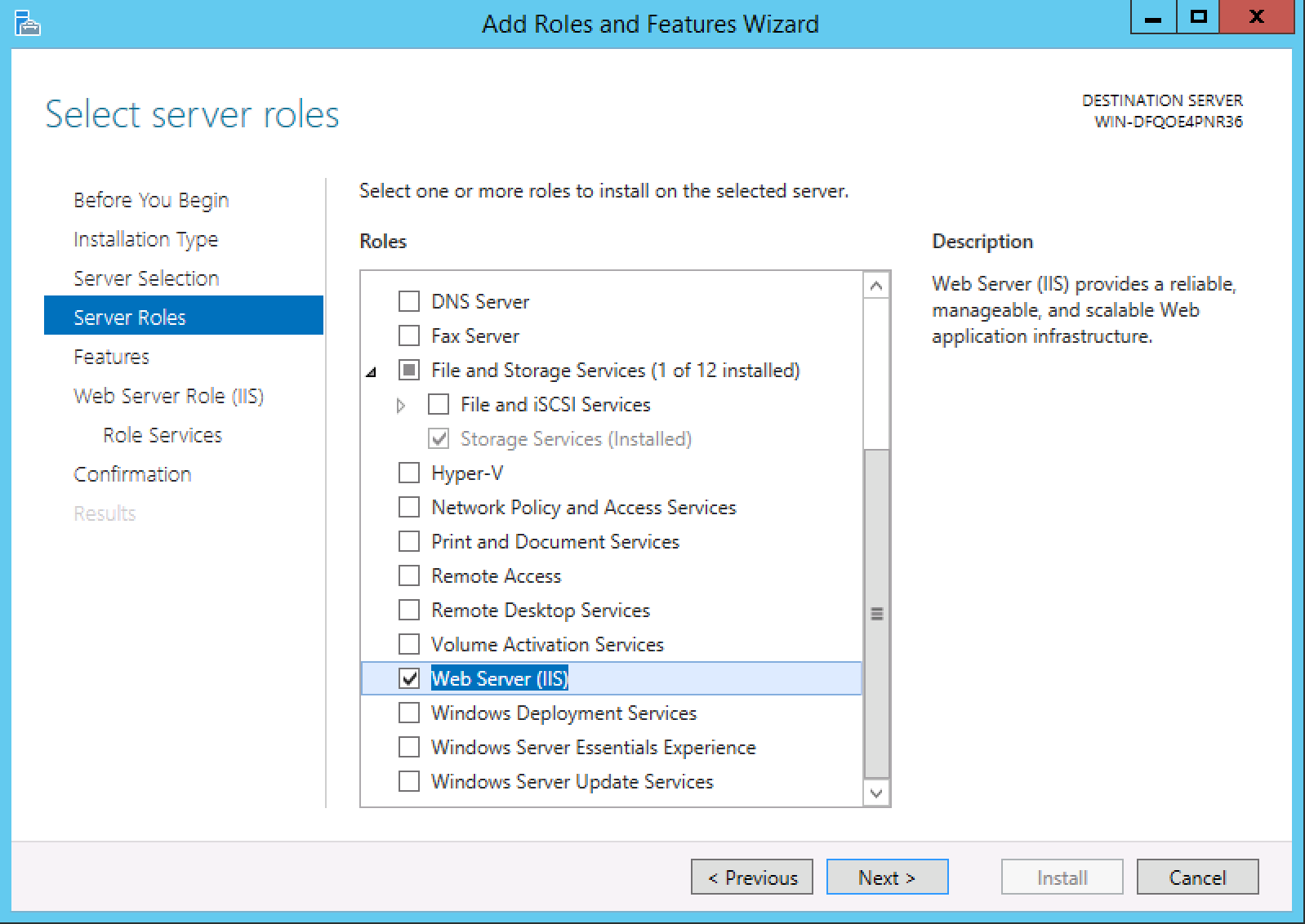
1. Using Server Manager:
- Open Server Manager.
- Navigate to "Roles and Features."
- Select the "Remove Roles and Features" option.
- Choose the server where IIS is installed.
- Expand the "Web Server (IIS)" role and uncheck all features.
- Follow the prompts to complete the uninstallation.
2. Using the Command Line:
- Open an elevated command prompt.
- Execute the following command:
servermanagercmd.exe -i -r Web-Server - Confirm the uninstallation by following the prompts.
Important Considerations
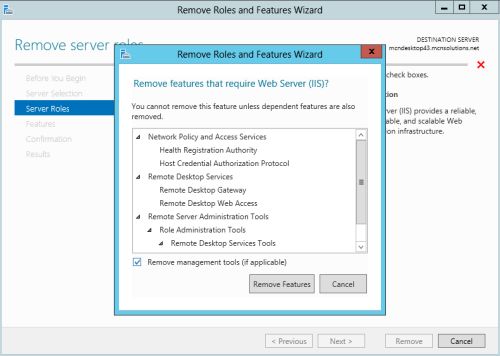
- Dependencies: Before proceeding with the removal, ensure that no other applications or services rely on IIS. Removing IIS without considering dependencies could disrupt other functionalities.
- Website Backups: If the server hosts websites, create backups of all website files and configurations before removing IIS.
-
Configuration Files: IIS stores configuration files in the
%systemroot%system32inetsrvdirectory. These files might contain crucial settings for other applications. Consider backing them up or carefully reviewing them before removal. - Restart Required: The removal process might require a server restart to complete.
Impact of Removing IIS
Removing IIS will have the following impacts:
- No Web Hosting: The server will no longer be able to host websites or web applications.
- No HTTP Service: The HTTP service will be disabled, and the server will not respond to HTTP requests.
- Removed Features: All IIS-related features, including web server functionalities, will be removed.
Benefits of Removing IIS
Removing IIS can provide several benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Eliminating potential attack vectors strengthens the server’s security posture.
- Resource Optimization: Freeing up system resources improves performance for other critical applications.
- Reduced Complexity: Simplifying the server environment by removing unused components reduces management overhead.
- Clean Transition: Removing IIS facilitates smooth server migration or decommissioning.
FAQs
Q: Can I re-install IIS after removing it?
A: Yes, IIS can be re-installed at any time by following the standard installation procedure through Server Manager or the command line.
Q: Will removing IIS affect other applications on the server?
A: It depends on the applications. If other applications rely on IIS functionalities, removing IIS might disrupt their operation. It is crucial to carefully assess dependencies before proceeding with the removal.
Q: What happens to my website data after removing IIS?
A: Removing IIS does not delete website data. The website files and databases will remain intact. However, the server will no longer serve them.
Q: Is it possible to remove IIS without restarting the server?
A: While possible in some cases, it is not recommended. Restarting the server ensures that all IIS components are completely removed and that the changes are applied correctly.
Tips for Removing IIS
- Thorough Planning: Carefully plan the removal process, considering dependencies, backups, and potential impacts.
- Documentation: Document the removal process, including any changes made to configurations or dependencies.
- Testing: After removing IIS, test other applications and services to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Re-installation: If you decide to re-install IIS in the future, refer to the documentation for the specific version of Windows Server you are using.
Conclusion
Removing IIS from a Windows Server can be a necessary step to improve security, optimize resources, or facilitate server transitions. By understanding the process, its implications, and best practices, administrators can ensure a smooth and successful removal. Remember to always consider dependencies, create backups, and test thoroughly after the removal to ensure system stability and functionality.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Removal of IIS on Windows Server: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!