Understanding Windows Server And Its Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Windows Server and its Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Windows Server and its Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Windows Server and its Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Windows Server and its Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide

Windows Server, a cornerstone of the Microsoft ecosystem, has been a dominant force in the server operating system market for decades. Its continual evolution reflects the ever-changing landscape of technology, offering businesses robust solutions for diverse computing needs. While the specific release "Windows Server 2025" does not yet exist, this article delves into the world of Windows Server, its historical trajectory, and the potential features and benefits that a future version might offer.
The Evolution of Windows Server: A Historical Perspective
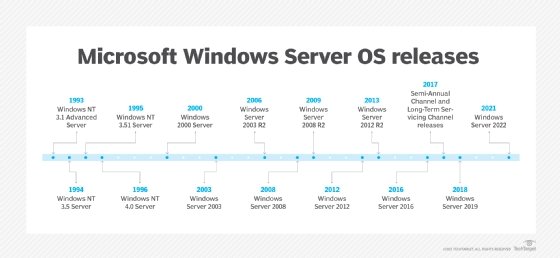
Windows Server’s journey began in 1993 with the release of Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server. This marked the beginning of a dedicated server operating system, distinct from its desktop counterpart. Over the years, Windows Server has undergone numerous transformations, each iteration introducing significant advancements:
- Windows NT 4.0 Server (1996): Brought Active Directory, a crucial tool for managing user accounts and network resources, into the fold.
- Windows 2000 Server (2000): Introduced Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) and enhanced security features.
- Windows Server 2003 (2003): Featured a more streamlined interface, improved security measures, and support for virtualization.
- Windows Server 2008 (2008): Emphasized virtualization capabilities, introducing Hyper-V, and offered a new graphical interface.
- Windows Server 2012 (2012): Introduced a cloud-centric approach, emphasizing features like Windows Azure integration and support for software-defined networking.
- Windows Server 2016 (2016): Focused on hybrid cloud environments, offering features like Nano Server, a minimal footprint server, and containerization support.
- Windows Server 2019 (2019): Furthered the hybrid cloud approach, introduced new security features, and enhanced containerization capabilities.
Windows Server 2025: Anticipating the Future
While the exact details of a hypothetical "Windows Server 2025" are speculative, several trends and evolving technologies suggest potential features and benefits.
1. Enhanced Security and Compliance: Cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated. A future version of Windows Server is likely to prioritize robust security measures, including:
- AI-powered threat detection and response: Leveraging artificial intelligence to proactively identify and neutralize threats.
- Zero-trust security model: Implementing strict access control policies, verifying user identities and device integrity at every interaction.
- Enhanced encryption and data protection: Strengthening data encryption capabilities and providing advanced data loss prevention mechanisms.
- Improved compliance with industry standards: Meeting the ever-evolving regulatory demands of various industries.
2. Deeper Cloud Integration: The shift towards cloud computing continues to accelerate. Windows Server 2025 might:
- Offer seamless integration with Microsoft Azure: Facilitating hybrid cloud deployments and leveraging cloud services for scalability and flexibility.
- Support multi-cloud environments: Allowing organizations to leverage services from multiple cloud providers, offering greater choice and control.
- Provide a platform for serverless computing: Enabling the execution of code without managing servers, offering cost-efficiency and scalability.
3. Advanced Virtualization and Containerization: Virtualization and containerization have revolutionized how applications are deployed and managed. Windows Server 2025 might:
- Enhance Hyper-V capabilities: Offering improved performance, scalability, and resource management for virtualized environments.
- Expand containerization support: Providing a robust platform for deploying and managing containerized applications, fostering agility and flexibility.
- Introduce new virtualization technologies: Exploring cutting-edge virtualization technologies like serverless computing and edge computing.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration: AI and ML are transforming various industries. A future Windows Server could:
- Offer built-in AI and ML capabilities: Enabling organizations to leverage these technologies for data analysis, predictive modeling, and automation.
- Provide a platform for AI/ML development: Facilitating the development and deployment of AI/ML-powered applications.
- Integrate with Microsoft’s AI platform: Leveraging Azure Cognitive Services and other AI tools for enhanced functionality.
5. Focus on Edge Computing: The rise of IoT and the need for data processing closer to the source are driving the growth of edge computing. Windows Server 2025 might:
- Offer optimized features for edge deployments: Supporting low-latency applications and providing secure and reliable edge computing solutions.
- Enable distributed computing capabilities: Allowing organizations to distribute workloads across edge devices, improving performance and resilience.
Understanding Windows Server: A Comprehensive Approach
While the future of Windows Server is inherently uncertain, understanding its historical trajectory and the trends shaping the technology landscape provides valuable insights. A hypothetical "Windows Server 2025" could offer significant advancements in security, cloud integration, virtualization, AI, and edge computing, empowering organizations to address future challenges and seize emerging opportunities.
FAQs
Q: What are the different editions of Windows Server?
A: Windows Server is offered in several editions tailored to specific needs:
- Windows Server Essentials: Designed for small businesses with up to 25 users.
- Windows Server Standard: Offers a comprehensive set of features for mid-sized organizations.
- Windows Server Datacenter: Provides advanced features for large enterprises and service providers.
- Windows Server Core: A minimal installation option, focusing on server functionality without a graphical interface.
- Windows Server Nano Server: An even smaller footprint option, ideal for containerized deployments.
Q: How do I install Windows Server?
A: Installing Windows Server typically involves:
- Downloading the ISO image: Obtain the installation file from the Microsoft website.
- Creating a bootable USB drive: Use a tool like Rufus or the Windows USB/DVD Download Tool to create a bootable USB drive.
- Booting from the USB drive: Configure your server’s BIOS to boot from the USB drive and follow the on-screen instructions.
Q: How do I manage a Windows Server?
A: Windows Server offers various tools for management:
- Server Manager: A graphical interface for managing server settings and applications.
- Windows PowerShell: A command-line interface for automating tasks and managing server configurations.
- Azure Portal: For managing Windows Server instances in Azure.
Tips
- Plan your deployment carefully: Before installing Windows Server, determine your specific needs and choose the appropriate edition and configuration.
- Implement strong security measures: Enable all security features and regularly update your system to mitigate potential threats.
- Back up your data regularly: Implement a robust backup strategy to protect your data from loss or corruption.
- Utilize automation tools: Leverage PowerShell and other automation tools to streamline server management tasks.
- Stay informed about updates: Microsoft regularly releases updates and patches for Windows Server. Keep your system up-to-date to ensure optimal performance and security.
Conclusion
Windows Server has played a pivotal role in the evolution of computing, providing businesses with reliable and scalable solutions. While the specific features of a future "Windows Server 2025" remain speculative, the technology’s historical trajectory and current trends suggest a future focused on enhanced security, deeper cloud integration, advanced virtualization, AI and ML integration, and edge computing. By understanding these trends and adapting to the evolving technological landscape, organizations can leverage the power of Windows Server to drive innovation and achieve their business objectives.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Windows Server and its Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!