Understanding Windows Server Forest Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Windows Server Forest Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Windows Server Forest Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Windows Server Forest Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Windows Server Forest Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
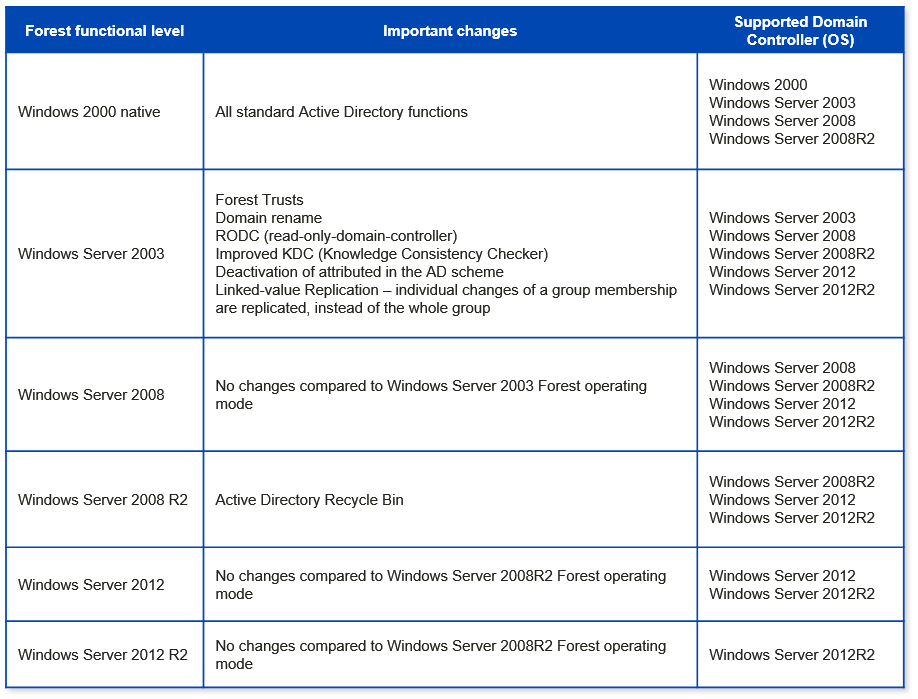
In the realm of Windows Server Active Directory (AD), a forest functional level represents a crucial element dictating the capabilities and features available to the entire domain structure. This concept plays a vital role in ensuring compatibility, security, and efficient management within an organization’s IT infrastructure. By understanding the different functional levels and their implications, administrators can optimize their AD environment for performance and leverage the latest advancements offered by Microsoft.
Delving into the Concept
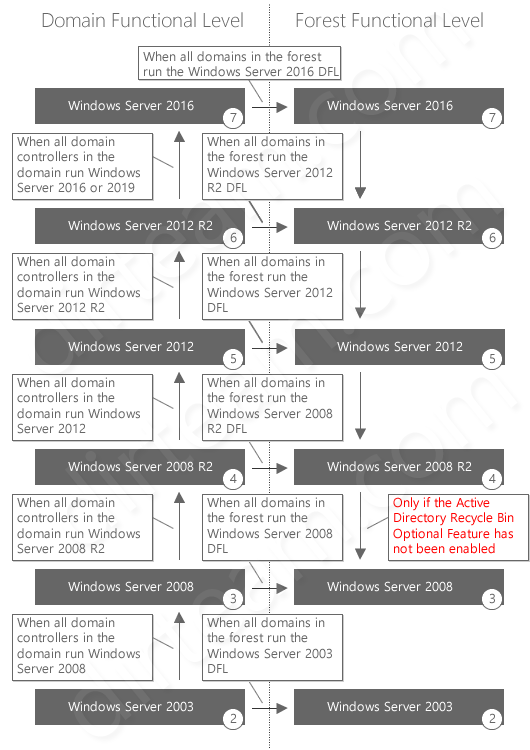
A Windows Server forest encompasses all the domains within a single instance of Active Directory. Each domain operates at a specific functional level, which reflects the version of Windows Server that introduced the features it supports. The forest functional level, however, dictates the highest level of functionality supported by the entire forest. This means that all domains within the forest are constrained by the capabilities of the lowest functional level.
The Evolution of Functional Levels
Over the years, Microsoft has introduced numerous advancements to Active Directory, each requiring a corresponding increase in the functional level to be fully utilized. This evolution has resulted in a hierarchical structure of functional levels, each building upon the previous ones.
Understanding the Functional Level Hierarchy
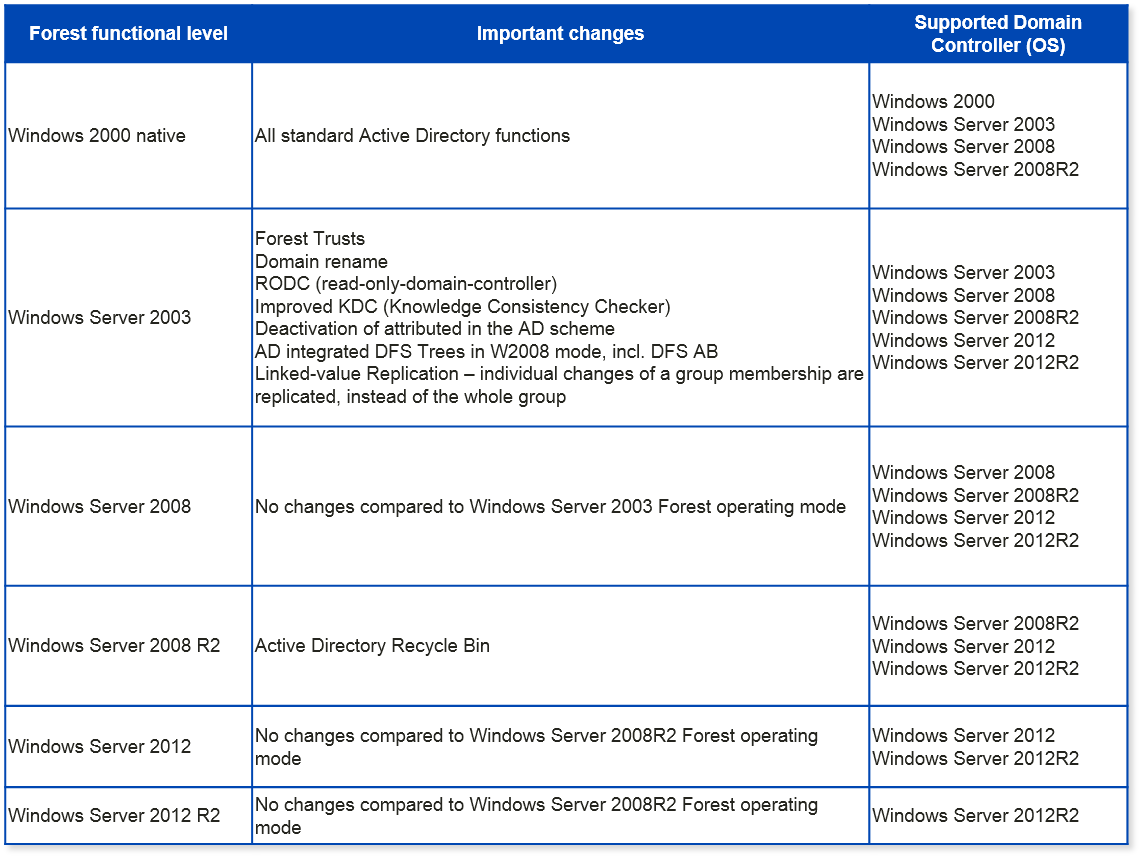
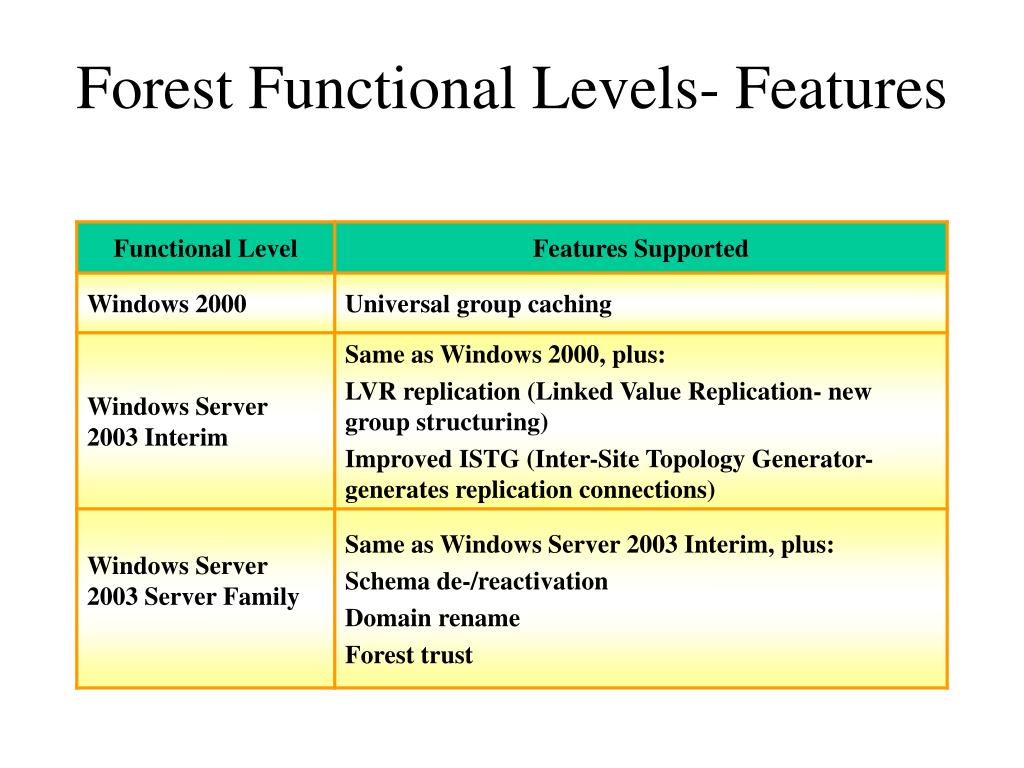
- Windows 2000 Forest Functional Level: This level provides the foundation for modern AD environments and supports essential features like Group Policy and Kerberos authentication.
- Windows Server 2003 Forest Functional Level: This level introduces enhancements such as Active Directory Recycle Bin and improved security features like fine-grained password policies.
- Windows Server 2008 Forest Functional Level: This level enables features like Active Directory Rights Management Services (RMS) and advancements in Group Policy management.
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Forest Functional Level: This level introduces support for Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) and enhancements in Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS).
- Windows Server 2012 Forest Functional Level: This level unlocks features like Domain Controller (DC) cloning, improved Group Policy management, and enhanced security features.
- Windows Server 2012 R2 Forest Functional Level: This level supports features like AD Recycle Bin for deleted objects, enhanced security features, and improvements in Group Policy management.
- Windows Server 2016 Forest Functional Level: This level enables features like Seamless Single Sign-On (SSO), enhanced security features, and improvements in Group Policy management.
- Windows Server 2019 Forest Functional Level: This level introduces features like Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) for improved security, enhancements in Group Policy management, and support for modern authentication protocols.
- Windows Server 2022 Forest Functional Level: This level brings advancements in security features, enhanced scalability, and support for cloud-based services.
The Importance of Functional Levels
The choice of forest functional level plays a crucial role in determining the capabilities and limitations of an AD environment. It impacts:
- Feature Availability: Raising the functional level unlocks access to newer features and functionalities introduced in subsequent versions of Windows Server.
- Security Posture: Each functional level introduces enhanced security features, ensuring better protection against threats and vulnerabilities.
- Compatibility: The functional level dictates the compatibility with different versions of Windows Server, ensuring smooth integration within the network.
- Performance and Scalability: Raising the functional level can improve performance and scalability, allowing for efficient management of large and complex environments.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Functional Level
The decision to raise the forest functional level should be carefully considered, taking into account several factors:
- Current Infrastructure: Assess the versions of Windows Server currently in use within the forest and their compatibility with the desired functional level.
- Feature Requirements: Identify the specific features and functionalities needed for the organization’s operations and their availability at different functional levels.
- Security Considerations: Evaluate the security enhancements offered by different functional levels and their relevance to the organization’s security posture.
- Impact on Existing Systems: Understand the potential impact of raising the functional level on existing systems and applications, ensuring compatibility and minimizing disruptions.
- Resource Availability: Consider the resources required to upgrade the forest functional level, including time, expertise, and potential hardware upgrades.
Raising the Forest Functional Level: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Assess Compatibility: Ensure that all domain controllers and clients within the forest are compatible with the desired functional level.
- Plan for Downtime: Raising the functional level can involve downtime, so schedule the process accordingly.
- Backup Data: Create a complete backup of the Active Directory database before proceeding with the upgrade.
- Raise the Domain Functional Level: Start by raising the functional level of each domain within the forest to the desired level.
- Raise the Forest Functional Level: Once all domains have been upgraded, raise the forest functional level to the desired level.
- Verify Functionality: After the upgrade, thoroughly test the functionality of all systems and applications to ensure they are working correctly.
FAQs on Windows Server Forest Functional Levels
1. What is the difference between a domain functional level and a forest functional level?
The domain functional level defines the capabilities available within a specific domain, while the forest functional level dictates the highest level of functionality supported by the entire forest. All domains within a forest are constrained by the lowest functional level.
2. Can I raise the forest functional level without raising the domain functional level?
No, raising the forest functional level requires all domains within the forest to be at least at the same functional level.
3. Can I lower the forest functional level?
It is not recommended to lower the forest functional level as it can lead to compatibility issues and loss of functionality.
4. What happens if I raise the forest functional level to a version not supported by all domain controllers?
If the forest functional level is raised to a version not supported by all domain controllers, the upgrade process will fail. It is crucial to ensure that all domain controllers meet the minimum requirements for the desired functional level.
5. What are the risks associated with raising the forest functional level?
Raising the forest functional level can introduce compatibility issues, disrupt existing systems, and require downtime. It is essential to carefully plan and test the upgrade process to mitigate these risks.
Tips for Managing Forest Functional Levels
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of the latest versions of Windows Server and the features they offer to make informed decisions about functional levels.
- Plan for the Future: Consider future requirements and growth when choosing a functional level to ensure sufficient capacity and flexibility.
- Test Thoroughly: Before raising the forest functional level, conduct thorough testing to ensure compatibility and minimize potential disruptions.
- Document Changes: Maintain detailed documentation of all changes made to the forest functional level, including the date, version, and any encountered issues.
- Seek Expert Assistance: For complex environments or when facing challenges, consult with experienced IT professionals or Microsoft support.
Conclusion
Understanding Windows Server forest functional levels is crucial for administrators seeking to optimize their Active Directory environment and leverage the latest advancements offered by Microsoft. By carefully considering the factors involved, planning for the upgrade process, and adhering to best practices, organizations can ensure a smooth transition to higher functional levels, unlocking new features and functionalities while maintaining compatibility and security within their IT infrastructure. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest functional levels and their implications will be essential for maximizing the benefits of Active Directory and ensuring a robust and efficient network environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Windows Server Forest Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!