Understanding Windows Server Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Windows Server Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Windows Server Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Windows Server Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Windows Server Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
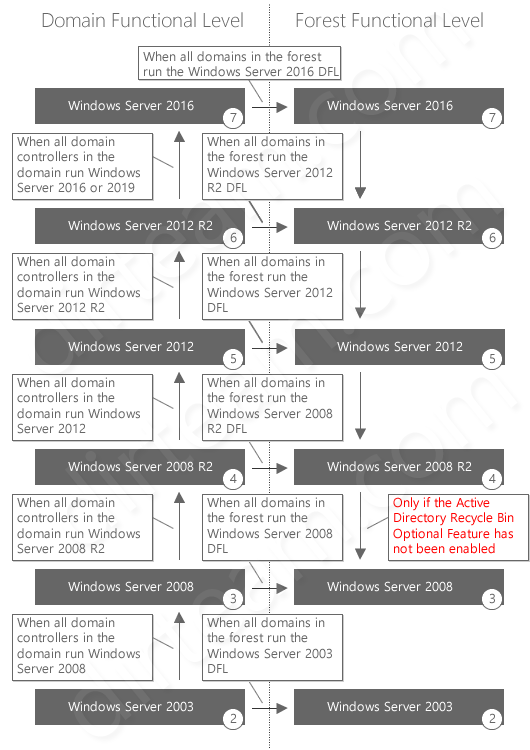
Windows Server functional levels are a crucial concept for administrators managing Active Directory domains. They represent a set of capabilities and features supported by a specific version of Windows Server operating system. Understanding these levels is essential for ensuring compatibility, optimizing performance, and leveraging the latest features available in your environment.
The Concept of Functional Levels:
Imagine a network of computers connected through Active Directory, each running a different version of Windows Server. To ensure seamless communication and functionality, a common ground needs to be established. This is where functional levels come into play.
Functional levels act as a "lowest common denominator" for the domain. They define the features and functionalities that all members of the domain, regardless of their individual operating system version, can utilize.
Types of Functional Levels:
Active Directory has two primary types of functional levels:
- Domain Functional Level (DFL): This level defines the features available within a specific domain. It impacts various aspects like group policy, security settings, and replication capabilities.
- Forest Functional Level (FFL): This level sets the minimum features supported across the entire Active Directory forest, which encompasses multiple domains. It ensures consistent functionality across all domains within the forest.
Why are Functional Levels Important?
- Compatibility: Functional levels ensure that all domain controllers and members can communicate and interact with each other, even if they run different versions of Windows Server.
- Feature Availability: Upgrading functional levels grants access to new features and capabilities introduced in later versions of Windows Server.
- Performance Optimization: By setting appropriate functional levels, administrators can optimize performance by utilizing features designed for specific versions of Windows Server.
- Security Enhancements: Newer functional levels often include enhanced security features, ensuring a more secure and robust Active Directory environment.
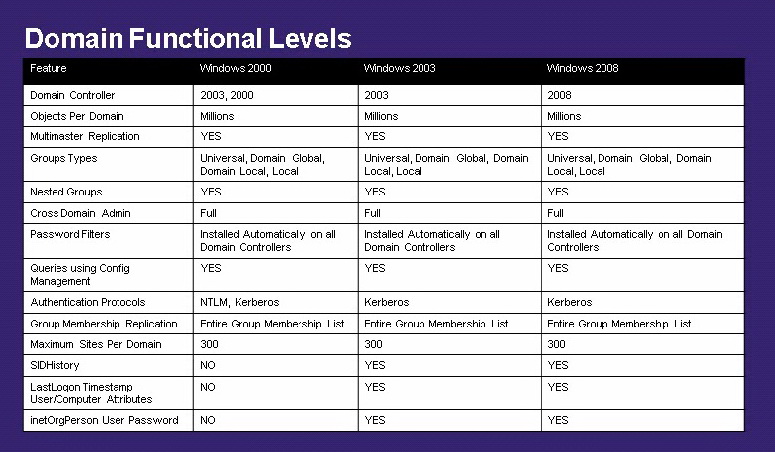
Common Functional Levels:
- Windows Server 2003: This level supports basic features and is typically used for legacy environments.
- Windows Server 2008: This level introduces new features like Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD RMS) and Group Policy Preferences.
- Windows Server 2008 R2: This level builds upon 2008, adding features like the ability to manage virtual machines (VMs) and enhanced security capabilities.
- Windows Server 2012: This level introduces features like Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) and Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS).
- Windows Server 2012 R2: This level expands upon 2012, adding features like Windows Server AppFabric and enhanced storage solutions.
- Windows Server 2016: This level brings significant advancements, including support for containers, Nano Server, and improved security measures.
- Windows Server 2019: This level builds upon 2016, introducing features like Windows Server Containers and improved security capabilities.
- Windows Server 2022: This level introduces features like Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) integration and enhanced security features.
Upgrading Functional Levels:
Upgrading functional levels allows you to take advantage of newer features and functionalities. However, it’s a critical process that requires careful planning and execution.
- Prerequisites: Ensure that all domain controllers in the forest or domain meet the minimum requirements for the target functional level.
- Impact Analysis: Evaluate the potential impact of the upgrade on existing applications, services, and user configurations.
- Testing: Thoroughly test the upgrade in a test environment before implementing it in production.
- Rollback Plan: Develop a plan to roll back the upgrade if unforeseen issues arise.
FAQs about Functional Levels:
Q: What happens if domain controllers have different functional levels?
A: The domain will operate at the lowest functional level among all domain controllers. This means you won’t be able to utilize features available in higher functional levels.
Q: Can I mix and match functional levels in a forest?
A: No, all domains within a forest must operate at the same forest functional level.
Q: What are the risks of upgrading functional levels?
A: Upgrading functional levels can potentially cause compatibility issues with older applications or services. It’s crucial to perform thorough testing and have a rollback plan in place.
Q: How do I determine the current functional levels?
A: You can use Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) or PowerShell cmdlets to view the current functional levels.
Tips for Managing Functional Levels:
- Stay Up-to-Date: Regularly review and update functional levels to leverage the latest features and security enhancements.
- Plan Upgrades Carefully: Thoroughly plan and test functional level upgrades to minimize potential disruptions.
- Document Changes: Keep detailed documentation of functional level changes for future reference.
- Consider a Test Environment: Use a test environment to evaluate the impact of functional level changes before implementing them in production.
Conclusion:
Windows Server functional levels are an essential aspect of managing Active Directory domains. Understanding their purpose, types, and implications is crucial for ensuring compatibility, optimizing performance, and leveraging the latest features available in your environment. By carefully planning and executing upgrades, administrators can take advantage of the benefits offered by newer functional levels while maintaining a stable and secure Active Directory environment.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Windows Server Functional Levels: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!