Understanding Windows Server License Downgrade Rights: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Windows Server License Downgrade Rights: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Windows Server License Downgrade Rights: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Windows Server License Downgrade Rights: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Windows Server License Downgrade Rights: A Comprehensive Guide
The concept of "downgrade rights" within the context of Windows Server licensing can seem complex, especially for those unfamiliar with the intricacies of software licensing agreements. However, understanding these rights can be crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure and maximize their licensing investments.
What are Downgrade Rights?
Downgrade rights, in the realm of Windows Server licensing, refer to the ability of a licensed user to utilize an older version of the software instead of the one originally purchased. This right is typically granted under specific circumstances and is subject to certain limitations outlined in the Microsoft Software License Agreement.
Windows Server 2022: The Starting Point
The most recent version of Windows Server, Windows Server 2022, offers a range of features and functionalities designed to cater to modern business needs. However, for various reasons, organizations may find it advantageous or necessary to utilize an earlier version of the operating system. This is where downgrade rights come into play.
Windows Server 2019: The Common Downgrade Option
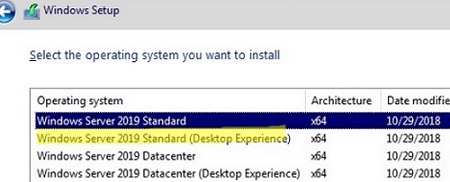
Windows Server 2019, the predecessor to Windows Server 2022, is a popular choice for downgrading. It offers a balance of features and compatibility with existing applications and infrastructure, making it a viable option for many organizations.
Downgrade Rights: A Spectrum of Possibilities
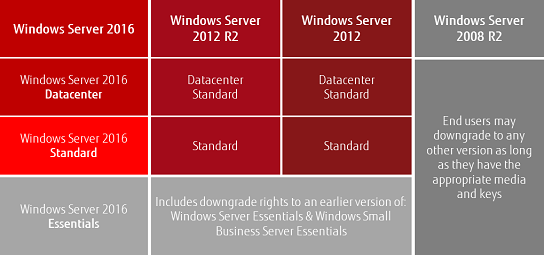
The specific downgrade rights available depend on the specific Windows Server license purchased. For instance, a Windows Server 2022 Datacenter license typically grants the right to downgrade to Windows Server 2019 Datacenter, while a Standard license permits downgrading to the corresponding Standard edition.
Why Downgrade? A Look at the Benefits
Downgrade rights offer a range of benefits for organizations, including:
- Cost Savings: Utilizing an older, less expensive version of Windows Server can significantly reduce licensing costs, particularly for large-scale deployments.
- Compatibility: In scenarios where existing applications or hardware are not compatible with the latest version of Windows Server, downgrading can ensure smooth integration and prevent compatibility issues.
- Security Considerations: While newer versions of Windows Server offer enhanced security features, some organizations may prefer the stability and known security posture of an older version, especially in environments with stringent security requirements.
- Hardware Limitations: Downgrading can be a practical solution when existing hardware does not meet the minimum system requirements for the latest version of Windows Server.
- Transitional Periods: Downgrade rights can be utilized during transitional periods, allowing organizations to gradually migrate their infrastructure to newer versions of Windows Server at their own pace.
Important Considerations: Navigating the Downgrade Landscape
While downgrade rights offer potential advantages, several considerations should be taken into account before making a decision:
- Software Support: Downgraded versions of Windows Server may have limited or no support from Microsoft, which could pose challenges in resolving technical issues or obtaining security updates.
- Feature Set: Downgraded versions may lack certain features or functionalities present in newer versions, potentially impacting the overall performance and capabilities of the operating system.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Older versions of Windows Server may be more vulnerable to security threats, necessitating proactive security measures and regular updates.
- License Compliance: It is crucial to ensure that the downgraded version of Windows Server is used in accordance with the terms of the original license agreement, avoiding potential legal complications.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Can I downgrade my Windows Server 2022 license to Windows Server 2016 or earlier versions?
A: The specific downgrade rights are outlined in the Microsoft Software License Agreement for your particular version of Windows Server. Typically, downgrade rights are limited to the immediate predecessor version. In most cases, downgrading to versions prior to Windows Server 2019 would require separate licensing.
Q: Do I need to pay additional fees for downgrading my Windows Server license?
A: Downgrade rights are typically included within the original license purchase. However, specific license terms and conditions may apply, so it is essential to review the agreement carefully.
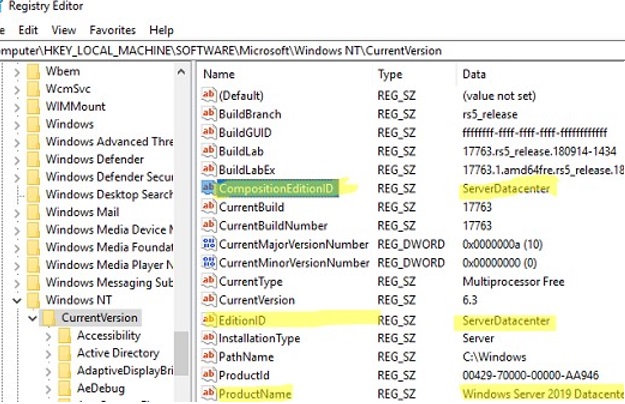
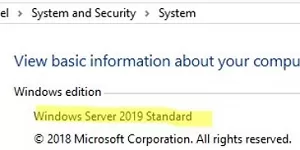
Q: How do I activate my downgraded version of Windows Server?
A: The activation process for downgraded versions is similar to that of the original version. However, you may need to use a different product key or activation method depending on the specific version and license type. Refer to the Microsoft documentation for detailed instructions.
Q: What happens if my downgraded version of Windows Server reaches its end of support?
A: Once a version of Windows Server reaches its end of support, Microsoft no longer provides security updates or technical support. It is highly recommended to upgrade to a supported version or consider other alternatives to ensure continued security and stability.
Tips for Effective Downgrade Management
- Thorough Research: Before making a decision to downgrade, conduct a thorough assessment of your specific needs, existing infrastructure, and compatibility requirements.
- License Agreement Review: Carefully review the Microsoft Software License Agreement for your version of Windows Server to understand the specific downgrade rights and limitations.
- Security Considerations: Implement robust security measures to mitigate potential vulnerabilities associated with older versions of Windows Server.
- Support Alternatives: Explore alternative support options, such as third-party vendors, if you are unable to obtain support from Microsoft for the downgraded version.
- Future Planning: Consider the long-term implications of downgrading, including potential future upgrades and compatibility issues.
Conclusion: A Strategic Approach to Downgrade Rights
Downgrade rights can be a valuable tool for organizations seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure and maximize their licensing investments. However, it is crucial to approach this strategy with careful planning and consideration. By understanding the specific downgrade rights available, assessing the potential benefits and risks, and implementing appropriate security measures, organizations can leverage downgrade rights effectively to achieve their IT objectives while ensuring compliance with Microsoft licensing agreements.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Windows Server License Downgrade Rights: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!