Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide

The landscape of server operating systems is constantly evolving, with Microsoft’s Windows Server releases playing a pivotal role. While the specific "Windows Server 2025" designation does not exist as an official release from Microsoft, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Windows Server licensing, encompassing key aspects relevant to any future release. This knowledge is crucial for organizations to effectively manage their server infrastructure, optimize costs, and ensure compliance with licensing agreements.
The Importance of Licensing
Windows Server licensing is a complex subject, but it’s essential to grasp its importance. Proper licensing ensures that organizations:
- Legally utilize Microsoft software: Using Windows Server without a valid license can result in significant legal and financial penalties.
- Access crucial support and updates: Licensed users are entitled to technical support, security patches, and software updates, ensuring their systems remain secure and functional.
- Maximize return on investment: Licensing models offer various options, allowing organizations to choose the most suitable approach based on their specific needs and budget.
Understanding License Types
Windows Server licensing is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Microsoft offers a variety of license types, each designed to cater to specific scenarios:
- Server Standard: The most common license type, suitable for general-purpose servers supporting multiple users and workloads.
- Server Datacenter: Designed for highly demanding environments, including virtualization and cloud deployments. Offers increased core licensing and flexibility.
- Server Essentials: An entry-level option for small businesses, offering features tailored to their specific needs.
- Server CAL (Client Access License): Allows users to access resources on a server. Required in addition to a server license for each user or device accessing the server.
Licensing Models: Exploring the Options
Microsoft offers various licensing models to accommodate different deployment strategies and budgetary considerations:
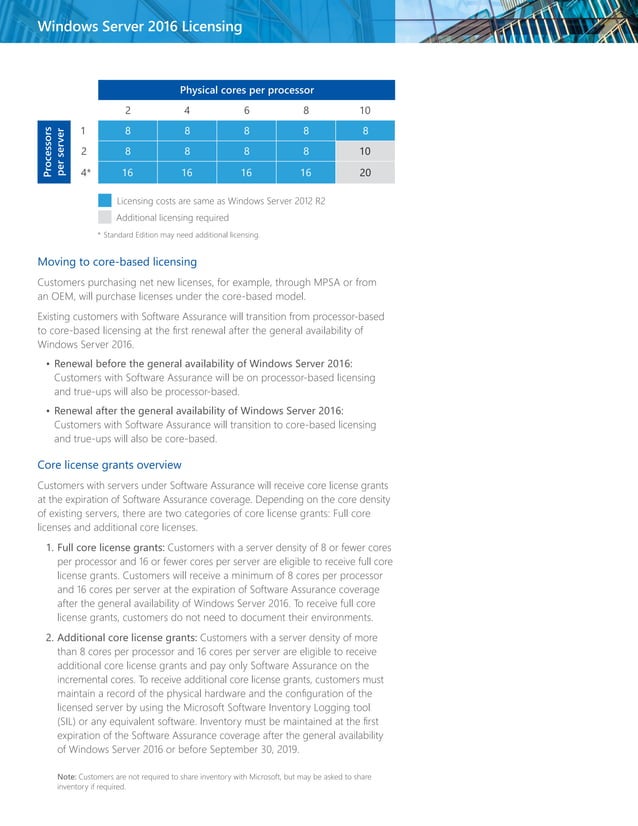
- Per-Processor Licensing: Each physical processor on a server requires a separate license.
- Per-Core Licensing: Each processor core requires a separate license, offering more flexibility for virtualization and cloud deployments.
- Server + CAL (Client Access License): Requires both a server license and a CAL for each user or device accessing the server.
- Software Assurance: An optional subscription service providing access to the latest software versions, updates, and other benefits.
Key Considerations for License Activation
When activating a Windows Server license, organizations must consider:
- License Type: Choose the license that best suits the server’s intended use and workload.
- Licensing Model: Select the licensing model that aligns with the organization’s deployment strategy and budget.
- Software Assurance: Evaluate the benefits of Software Assurance and its potential cost-saving opportunities.
- Activation Method: Familiarize yourself with the activation process and required documentation.
FAQs: Addressing Common Licensing Queries
Q: What happens if I don’t activate my Windows Server license?
A: Unlicensed Windows Server usage can lead to legal and financial repercussions, including fines and potential software removal.
Q: Can I use a Server Standard license for virtualization?
A: Server Standard licenses can be used for virtualization, but there are limitations on the number of virtual machines (VMs) allowed. Server Datacenter licenses offer greater flexibility for virtualization deployments.
Q: How often do I need to renew my Windows Server license?
A: License renewal frequency depends on the specific licensing model chosen. Software Assurance provides ongoing access to the latest versions and updates.
Q: Can I transfer my Windows Server license to a different server?
A: License transferability depends on the specific license type and licensing model. Consult Microsoft documentation for detailed information.
Tips for Effective License Management
- Inventory and track all licenses: Maintain a comprehensive inventory of all Windows Server licenses, including type, model, and activation details.
- Regularly review licensing needs: Assess server usage and workload patterns to ensure licenses remain aligned with actual requirements.
- Explore licensing options: Research different licensing models and choose the one that optimizes cost and efficiency.
- Engage with Microsoft partners: Utilize the expertise of Microsoft partners to navigate complex licensing scenarios and ensure compliance.
Conclusion: Optimizing Server Infrastructure
Understanding Windows Server licensing is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their server infrastructure, minimize costs, and ensure legal compliance. By carefully evaluating licensing options, leveraging available resources, and adhering to best practices, organizations can create a robust and secure server environment that supports their business goals.
Remember, staying informed about the latest licensing updates and engaging with Microsoft partners can help organizations navigate the complexities of Windows Server licensing and make informed decisions that drive efficiency and cost-effectiveness.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
