Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Focus On 16-Core Configurations
Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Focus on 16-Core Configurations
Related Articles: Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Focus on 16-Core Configurations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Focus on 16-Core Configurations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Focus on 16-Core Configurations
Microsoft Windows Server, a ubiquitous operating system for server environments, offers various licensing models to cater to diverse needs. Among these, the 16-core license model stands out as a popular choice for organizations with moderate to high computational demands. This article delves into the intricacies of this licensing model, exploring its key features, benefits, and considerations.
The Foundation of Windows Server Licensing: Core-Based Licensing
Microsoft’s shift to a core-based licensing model for Windows Server has significantly altered the landscape of server deployments. This model, introduced with Windows Server 2012, abandons the traditional per-processor licensing scheme in favor of a more granular, core-centric approach.
Understanding the 16-Core License Model
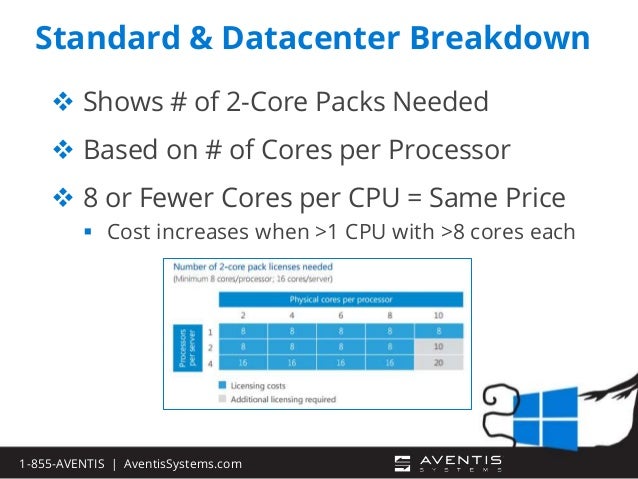
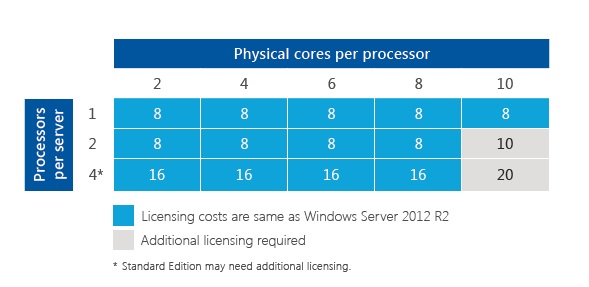
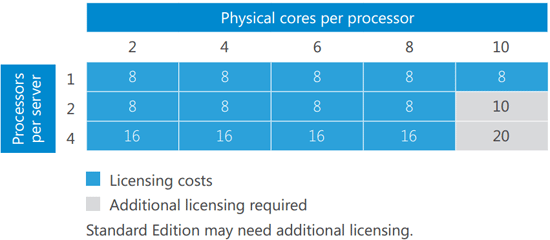
The 16-core license model, as its name suggests, grants rights to utilize a specific number of processor cores within a server. In this case, it allows for the use of up to 16 physical processor cores. This licensing model is typically associated with servers that offer a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness.
Benefits of the 16-Core License Model
- Scalability: The 16-core license model offers a scalable solution, allowing organizations to adapt to changing computational demands. As workloads grow, additional servers with 16-core licenses can be deployed, ensuring smooth performance.
- Cost-Efficiency: This licensing model can be more cost-effective than purchasing per-processor licenses, especially for servers with a moderate number of cores.
- Flexibility: The 16-core license model provides flexibility, allowing organizations to choose servers with specific core configurations that align with their budget and performance requirements.
Considerations for Implementing the 16-Core License Model
- Workload Requirements: Organizations need to carefully evaluate their workload requirements to determine if a 16-core license model is suitable. High-demand applications might require more cores, while less intensive workloads might be adequately served by a lower core count.
- Server Hardware: Choosing the right server hardware is crucial when implementing a 16-core license model. The server should be equipped with processors that support the required number of cores and offer sufficient memory and storage capacity.
- Licensing Terms: It’s essential to understand the specific terms and conditions associated with the 16-core license model. This includes understanding the permissible uses, limitations, and renewal procedures.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the key differences between per-processor and core-based licensing models?
A: Per-processor licensing grants rights to use a complete processor, regardless of the number of cores it contains. Core-based licensing, on the other hand, provides rights to use a specific number of cores, regardless of the number of processors they belong to.
Q: Can I use a 16-core license on a server with more than 16 cores?
A: No. A 16-core license only grants rights to use 16 physical cores. Using more than 16 cores without the appropriate licenses would constitute a violation of the licensing agreement.
Q: What are the implications of virtualization when using a 16-core license model?
A: Virtualization can introduce complexities in licensing. In general, each virtual machine running on a server requires its own separate license. However, specific licensing rules apply to virtual environments, and it’s essential to consult Microsoft’s documentation for detailed guidance.
Q: How can I optimize my server configuration for a 16-core license model?
A: Optimizing your server configuration for a 16-core license model involves several considerations:
- Processor Selection: Choose processors with a high core count and clock speed that align with your workload requirements.
- Memory Management: Ensure sufficient memory is available to accommodate the running applications and virtual machines.
- Storage Capacity: Select storage solutions that offer adequate capacity and performance to handle the data generated by your workloads.
Tips for Effective Implementation
- Thorough Planning: Before deploying a 16-core license model, conduct a comprehensive assessment of your current and future workload requirements.
- License Management: Implement robust license management practices to track license usage, ensure compliance, and avoid potential licensing issues.
- Regular Monitoring: Monitor server performance and resource utilization regularly to identify any potential bottlenecks and adjust server configurations as needed.
Conclusion
The 16-core license model for Windows Server provides a cost-effective and scalable solution for organizations with moderate to high computational demands. Understanding the nuances of this licensing model, including its benefits, considerations, and licensing terms, is crucial for successful implementation. By carefully planning, optimizing server configurations, and adhering to licensing guidelines, organizations can leverage this model to enhance their server environments and achieve optimal performance.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Windows Server Licensing: A Focus on 16-Core Configurations. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
