Understanding Windows Server Licensing In 2023 And Beyond
Understanding Windows Server Licensing in 2023 and Beyond
Related Articles: Understanding Windows Server Licensing in 2023 and Beyond
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Windows Server Licensing in 2023 and Beyond. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Windows Server Licensing in 2023 and Beyond
![Microsoft Windows Server licensing changes [2023] - SCHNEIDER IT MANAGEMENT](https://www.schneider.im/media/2023/04/SCHNEIDER-IT-MANAGEMENT-2023-04-14-Update-Windows-Server-licensing-changes-1024x658.jpg)
The landscape of server operating systems is constantly evolving, and Microsoft’s Windows Server remains a dominant player in the enterprise space. Understanding the licensing models and considerations for Windows Server is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their infrastructure and maximize return on investment. This article delves into the intricacies of Windows Server licensing, providing insights into the various options available, factors influencing licensing choices, and key considerations for successful deployment.
Windows Server Licensing Models: A Comprehensive Overview
Microsoft offers several licensing models for Windows Server, each tailored to specific deployment scenarios and organizational needs. Understanding these models is paramount to selecting the most cost-effective and efficient licensing solution.
1. Server Client Access Licenses (CALs):
- Core-based Licensing: This model is based on the number of physical processor cores utilized by the server. Each core requires a corresponding CAL.
- User CALs: These licenses are assigned to individual users who access the server.
- Device CALs: These licenses are assigned to devices, such as computers or mobile devices, that access the server.
- External Connector License: This license is required for each connection to the server from an external user or device.
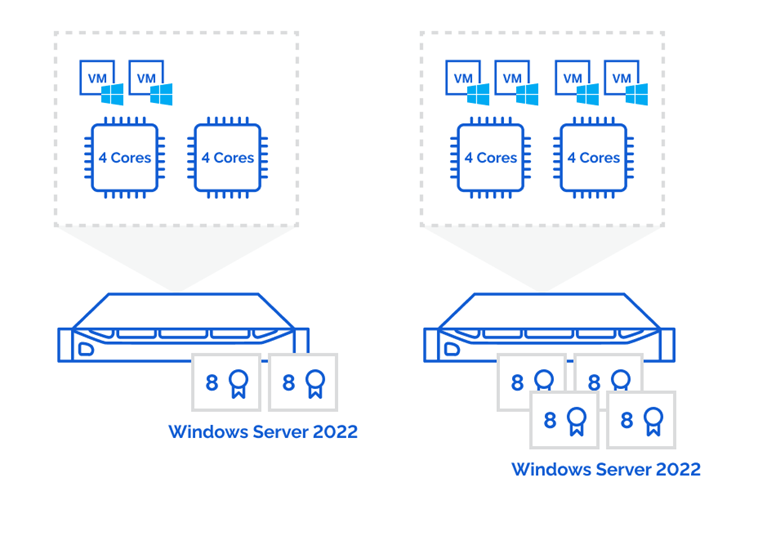
2. Datacenter Edition Licensing:
- Unlimited User/Device CALs: This edition grants organizations unlimited access for users and devices to the server.
- Virtualization Rights: Datacenter edition licenses allow for the virtualization of the server operating system, facilitating the deployment of multiple virtual machines on a single physical server.
3. Standard Edition Licensing:
- Limited User/Device CALs: This edition offers a limited number of user or device CALs per server.
- Virtualization Rights: Standard edition licenses allow for the virtualization of the server operating system, but with limitations on the number of virtual machines that can be deployed.
4. Windows Server Subscription:
- Cloud-focused Licensing: This model provides access to Windows Server through a subscription-based service, offering flexibility and scalability.
- Azure Hybrid Benefits: Subscription licenses often include benefits for Azure services, enabling seamless integration between on-premises and cloud environments.
Factors Influencing Windows Server Licensing Choices
Several factors influence the selection of the most appropriate Windows Server licensing model:
- Organizational Size and Structure: Large enterprises with a distributed workforce may require a different licensing approach compared to smaller organizations with centralized operations.
- Deployment Environment: The nature of the deployment environment, including physical or virtualized infrastructure, dictates the licensing model.
- Application Requirements: The specific applications and services hosted on the server influence the choice of licensing model, as certain features and capabilities may be required.
- Budgetary Constraints: Licensing costs vary significantly across different models. Organizations need to carefully evaluate their budget and licensing requirements to select the most cost-effective option.
- Future Scalability: Organizations must consider their future growth and scalability needs when selecting a licensing model, ensuring flexibility and adaptability.
Key Considerations for Windows Server Licensing
- Software Assurance: Software Assurance (SA) is an optional subscription that provides access to ongoing software updates, upgrades, and support services.
- Virtualization Rights: Carefully evaluate the virtualization rights associated with different licensing models, especially when deploying virtual machines.
- Server Core Installation: Organizations can choose to install Windows Server in "Server Core" mode, a minimal installation that reduces licensing costs and simplifies management.
- Third-Party Software Compatibility: Ensure that third-party software applications are compatible with the chosen Windows Server licensing model and edition.
FAQs Regarding Windows Server Licensing
1. What is the difference between User CALs and Device CALs?
- User CALs are assigned to individual users who access the server, while Device CALs are assigned to devices, such as computers or mobile devices, that access the server.
2. Can I use a single Windows Server license for multiple virtual machines?
- The answer depends on the licensing model and edition. Datacenter edition licenses typically offer unlimited virtualization rights, while Standard edition licenses may have limitations on the number of virtual machines that can be deployed.
3. What are the benefits of Software Assurance?
- Software Assurance provides access to ongoing software updates, upgrades, and support services, ensuring that organizations have the latest features and security patches.
4. How can I determine the appropriate Windows Server licensing model for my organization?
- Carefully assess the factors influencing licensing choices, including organizational size, deployment environment, application requirements, budgetary constraints, and future scalability needs.
5. What are the consequences of using an unlicensed Windows Server?
- Using an unlicensed Windows Server is a violation of Microsoft’s licensing agreement and can result in legal penalties, fines, and potential software audits.
Tips for Managing Windows Server Licensing
- Maintain Accurate Inventory: Keep detailed records of all server licenses, editions, and associated CALs.
- Regularly Review Licensing Requirements: Periodically assess your licensing needs and ensure that your current licenses are sufficient.
- Consider Software Assurance: Explore the benefits of Software Assurance to ensure access to ongoing updates, upgrades, and support services.
- Optimize Virtualization Deployment: Utilize virtualization effectively to maximize the utilization of server licenses and reduce licensing costs.
- Consult with Microsoft Partners: Seek guidance from Microsoft partners for expert advice on licensing models and deployment strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding Windows Server licensing models and considerations is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their infrastructure and maximize return on investment. By carefully evaluating the available licensing options, considering factors influencing licensing choices, and following best practices for licensing management, organizations can ensure compliance, minimize costs, and effectively leverage the power of Windows Server.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Windows Server Licensing in 2023 and Beyond. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!