Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) In The Modern IT Landscape
Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) in the Modern IT Landscape
Related Articles: Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) in the Modern IT Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) in the Modern IT Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) in the Modern IT Landscape
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) in the Modern IT Landscape
- 3.1 The Importance of Effective Update Management
- 3.2 The Role of WSUS in Update Management
- 3.3 The Limitations of WSUS in the Modern IT Environment
- 3.4 Exploring Alternative Solutions
- 3.5 The Future of WSUS
- 3.6 FAQs Regarding WSUS
- 3.7 Tips for Effective WSUS Management
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) in the Modern IT Landscape
Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) has been a cornerstone of Microsoft’s update management strategy for years, providing a centralized platform for distributing and managing software updates for Windows operating systems and applications. While WSUS has served its purpose well, the evolving IT landscape necessitates a deeper understanding of its role and potential limitations in the context of modern technology. This article explores the significance of WSUS in the contemporary IT environment, highlighting its strengths, limitations, and the need for alternative or complementary solutions.
The Importance of Effective Update Management
In today’s world, where cyber threats are constantly evolving and vulnerabilities are continuously discovered, maintaining a secure and up-to-date IT infrastructure is paramount. Software updates, including security patches, bug fixes, and feature enhancements, are essential to ensure the stability, security, and functionality of systems.
Failing to implement a robust update management strategy can lead to:
- Increased vulnerability to security breaches: Outdated software is a prime target for attackers, leaving systems vulnerable to malware, ransomware, and other exploits.
- System instability and performance issues: Bugs and vulnerabilities can cause system crashes, slowdowns, and other performance problems.
- Compliance violations: Many regulatory bodies mandate the timely application of security updates to ensure compliance with industry standards.
- Increased downtime and operational disruptions: Unpatched systems can lead to unexpected outages, disrupting business operations and impacting productivity.
The Role of WSUS in Update Management
WSUS plays a crucial role in addressing these challenges by providing a centralized platform for managing software updates across an entire network. It allows administrators to:
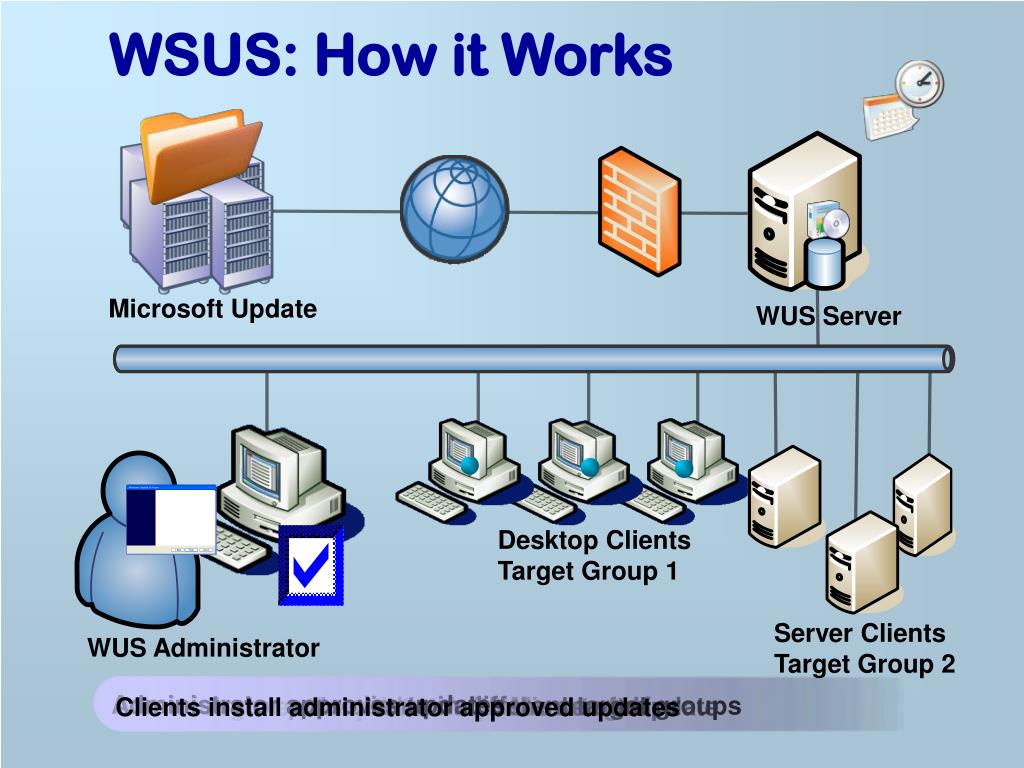
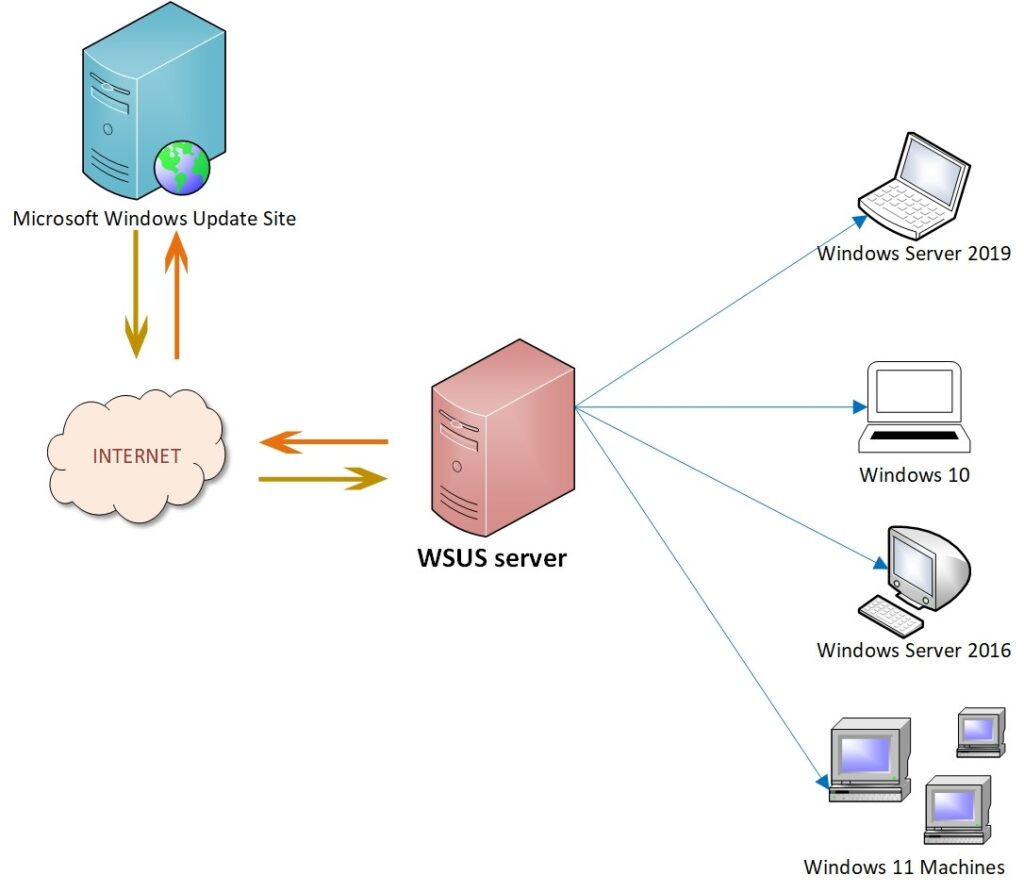
- Download updates from Microsoft Update: WSUS acts as a proxy server, downloading updates from Microsoft Update and storing them locally. This eliminates the need for each client to individually download updates, reducing network bandwidth consumption and improving update deployment speed.
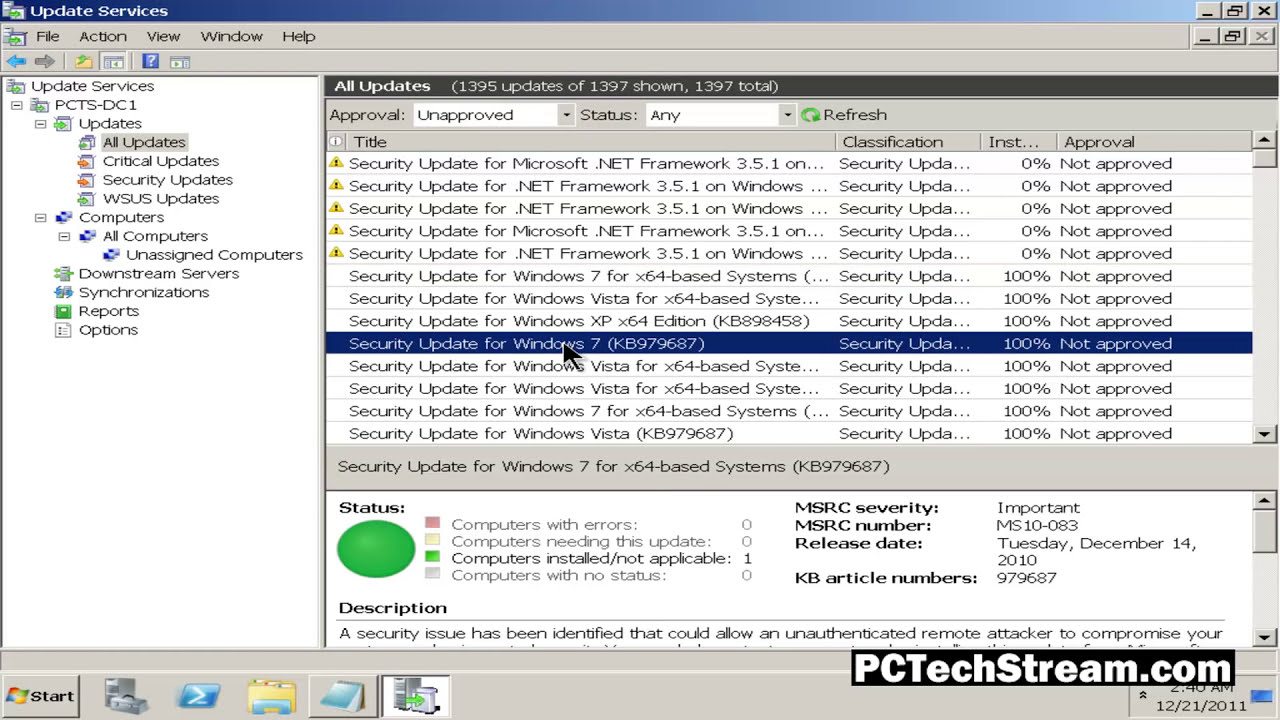
- Approve and deploy updates: Administrators can review updates, approve them for deployment, and schedule their distribution to client machines. This allows for better control over the update process and ensures that only approved updates are deployed.
- Create update groups: WSUS allows administrators to create groups of computers based on their roles, operating systems, or other criteria. This enables targeted update deployment, ensuring that the right updates are delivered to the appropriate machines.
- Report on update status: WSUS provides comprehensive reporting capabilities, allowing administrators to track the status of updates, identify machines that have not been updated, and troubleshoot any issues.
The Limitations of WSUS in the Modern IT Environment
While WSUS has been a valuable tool for many organizations, it faces challenges in the context of modern IT trends:
- Cloud migration: As more organizations move to the cloud, traditional on-premises solutions like WSUS become less relevant. Cloud-based services offer a more scalable and flexible approach to update management.
- Complex IT environments: Modern IT environments often consist of a mix of on-premises and cloud resources, making it challenging to manage updates across different platforms using WSUS.
- Limited automation capabilities: WSUS offers limited automation capabilities, requiring manual intervention for tasks such as update approval and deployment.
- Security considerations: WSUS relies on a traditional on-premises infrastructure, which can pose security risks if not properly configured and maintained.
Exploring Alternative Solutions
The limitations of WSUS have prompted organizations to explore alternative solutions, such as:
- Cloud-based update management services: Services like Microsoft Endpoint Manager (formerly Intune) provide a comprehensive cloud-based platform for managing updates, configurations, and other aspects of device management. These services offer greater scalability, flexibility, and automation capabilities compared to WSUS.
- Third-party update management solutions: A variety of third-party solutions are available, offering features like automated update deployment, patch analysis, and vulnerability scanning. These solutions can complement or even replace WSUS, depending on the specific needs of an organization.
The Future of WSUS
While WSUS remains a viable option for managing updates in certain environments, its future is uncertain. The shift towards cloud computing and the increasing demand for automated and scalable solutions suggest that WSUS will gradually fade into the background.
However, WSUS is likely to continue playing a role in managing updates for on-premises servers and legacy systems. Organizations may choose to use WSUS in conjunction with cloud-based solutions to manage a hybrid IT environment.
FAQs Regarding WSUS
1. What is the difference between WSUS and Microsoft Update?
Microsoft Update is a centralized service that provides software updates for Windows operating systems and applications. WSUS acts as a proxy server, downloading updates from Microsoft Update and storing them locally for distribution within a network.
2. How does WSUS work?
WSUS works by downloading updates from Microsoft Update and storing them locally. It then allows administrators to approve and deploy these updates to client machines within the network.
3. What are the benefits of using WSUS?
WSUS provides several benefits, including:
- Centralized update management: Allows administrators to manage updates for all client machines from a single console.
- Reduced network bandwidth consumption: Downloads updates only once and distributes them locally, reducing bandwidth usage.
- Controlled update deployment: Enables administrators to approve and schedule updates before they are deployed to client machines.
- Comprehensive reporting: Provides detailed reports on update status, allowing administrators to track progress and identify issues.
4. What are the limitations of WSUS?
WSUS has several limitations, including:
- Limited scalability: Can struggle to manage updates for large networks or complex IT environments.
- Limited automation capabilities: Requires manual intervention for tasks such as update approval and deployment.
- Security considerations: Relies on a traditional on-premises infrastructure, which can pose security risks if not properly configured and maintained.
5. What are the alternatives to WSUS?
Alternatives to WSUS include:
- Cloud-based update management services: Services like Microsoft Endpoint Manager (formerly Intune) offer a comprehensive cloud-based solution for managing updates, configurations, and other aspects of device management.
- Third-party update management solutions: A variety of third-party solutions are available, offering features like automated update deployment, patch analysis, and vulnerability scanning.
6. Should I use WSUS or a cloud-based solution?
The choice between WSUS and a cloud-based solution depends on the specific needs of an organization. If an organization has a small, on-premises network and does not require advanced automation or scalability, WSUS may be a suitable option. However, for organizations with large, complex IT environments or a need for greater flexibility and automation, a cloud-based solution is likely to be a better choice.
7. Can I use WSUS with a cloud-based environment?
Yes, it is possible to use WSUS with a cloud-based environment, but it can be challenging to manage updates across different platforms. Organizations may choose to use WSUS for on-premises servers and a cloud-based solution for cloud resources.
8. How do I configure WSUS?
Configuring WSUS involves several steps, including:
- Installing WSUS: Download and install the WSUS server role on a Windows Server machine.
- Configuring the WSUS server: Configure the WSUS server to connect to Microsoft Update and define the update content to be synchronized.
- Creating update groups: Create groups of computers based on their roles, operating systems, or other criteria.
- Approving and deploying updates: Review updates, approve them for deployment, and schedule their distribution to client machines.
9. How do I troubleshoot WSUS issues?
Troubleshooting WSUS issues involves:
- Reviewing logs: Check the WSUS logs for error messages and other information.
- Verifying connectivity: Ensure that the WSUS server can connect to Microsoft Update and that client machines can connect to the WSUS server.
- Checking update status: Verify the status of updates and identify any machines that have not been updated.
10. Is WSUS still relevant in the modern IT landscape?
While WSUS remains a viable option for managing updates in certain environments, its future is uncertain. The shift towards cloud computing and the increasing demand for automated and scalable solutions suggest that WSUS will gradually fade into the background. However, WSUS is likely to continue playing a role in managing updates for on-premises servers and legacy systems.
Tips for Effective WSUS Management
- Plan and configure WSUS carefully: Before deploying WSUS, carefully plan the configuration to ensure it meets the specific needs of the organization.
- Create appropriate update groups: Group computers based on their roles, operating systems, or other criteria to ensure targeted update deployment.
- Approve updates carefully: Review updates before approving them for deployment to ensure that they are compatible with the organization’s systems.
- Schedule updates strategically: Schedule updates during off-peak hours to minimize disruption to users.
- Monitor update status regularly: Monitor the status of updates to identify any issues and troubleshoot them promptly.
- Keep WSUS up to date: Regularly update WSUS to ensure that it is running the latest version and that it is compatible with the latest operating systems and applications.
- Consider alternative solutions: If WSUS is not meeting the needs of the organization, consider exploring alternative solutions like cloud-based update management services or third-party update management tools.
Conclusion
Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) has played a vital role in managing software updates for Windows operating systems and applications. While it continues to be a valuable tool for certain organizations, the evolving IT landscape demands a more flexible and scalable approach to update management. Cloud-based solutions and third-party tools offer greater automation, scalability, and security features, making them increasingly attractive alternatives to WSUS.
As organizations continue to embrace cloud computing and adopt more sophisticated IT strategies, WSUS’s role in update management will likely diminish. However, it will continue to be relevant for managing updates for on-premises servers and legacy systems. By understanding the strengths, limitations, and alternatives to WSUS, organizations can make informed decisions about their update management strategy and ensure that their systems are secure, stable, and up to date.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) in the Modern IT Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!